The 50 Most-cited Articles in Gastroenterology and Hepatology from Mainland China
- PMID: 28367203
- PMCID: PMC5368312
- DOI: 10.12669/pjms.331.12286
The 50 Most-cited Articles in Gastroenterology and Hepatology from Mainland China
Abstract
Objective: To identify and analyze the 50 most-cited gastroenterology and hepatology articles originating from mainland China.
Methods: We utilized the 2015 edition of Journal Citation Reports and PubMed to determine the 50 most-cited gastroenterology and hepatology articles from 75 professional journals and four leading journals in clinical medicine, which are The New England Journal of Medicine, The Lancet, The Journal of the American Medical Association, and The British Medical Journal. Then we excluded the articles written outside mainland China and collected the basic information, including the title, authors, year of publication, source journal, city, institution, number of citations, and topic of the research.
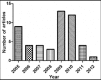
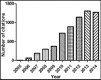
Results: The number of citations for the top 50 papers ranged from 279 to 89 (mean, 129). These articles were published between 2005 and 2012, in which 2009 was the year with the largest number of highly cited papers(13). All articles were published in 15 journals. The journal Hepatology published the largest number of articles(21), followed by Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology(4), Journal of Hepatology(4) and World Journal of Gastroenterology(4). The top 50 articles originated mainly from Shanghai(20), Guangzhou(13) and Beijing(6). Sun Yat-sen University produced most highly cited papers(10). The number of basic research was far more than clinical research, of which the ratio was about 1.78(32:18). In all these articles, hepatocellular carcinoma was the most-discussed topic(19), followed by hepatitis B virus(8) and endoscopic(5).
Conclusions: Although a large gap remains between mainland China and the global community, the gastroenterology and hepatology research from China is gradually recognized by the world.
Keywords: Bibliometrics; Gastroenterology and Hepatology; Mainland China; Science Citation Index; Web of Science.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interest: The authors report no conflicts of interest. The authors alone are responsible for the content and writing of the article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The 50 Most-cited Articles in Orthopaedic Surgery From Mainland China.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015 Jul;473(7):2423-30. doi: 10.1007/s11999-015-4132-1. Epub 2015 Jan 15. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015. PMID: 25589444 Free PMC article.
-
Integrity of the editing and publishing process is the basis for improving an academic journal's Impact Factor.World J Gastroenterol. 2022 Nov 21;28(43):6168-6202. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i43.6168. World J Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 36483155 Free PMC article.
-
[Citation analysis of the Chinese Journal of Hepatology (Zhonghua Ganzangbing Zazhi) in the year 2005].Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2006 Jun;14(6):473-6. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2006. PMID: 16937588 Chinese.
-
Scientific publications in gastroenterology and hepatology journals from Chinese authors in various parts of North Asia: 10-year survey of literature.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008 Mar;23(3):374-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2008.05329.x. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008. PMID: 18318822 Review.
-
Citation classics: Top 50 cited articles in 'respiratory system'.Respirology. 2013 Jan;18(1):71-81. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1843.2012.02262.x. Respirology. 2013. PMID: 22978302 Review.
Cited by
-
The 100 Top-Cited Systematic Reviews/Meta-Analyses on Diabetic Research.J Diabetes Res. 2020 Sep 11;2020:5767582. doi: 10.1155/2020/5767582. eCollection 2020. J Diabetes Res. 2020. PMID: 33005691 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Reforming research in China. Lancet. 2007;369:880. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60419-X. - PubMed
-
- Liu W, Tang L, Gu M, Hu G. Feature report on China: a bibliometric analysis of China-related articles. Scientometrics. 2014;102(1):503–517.
-
- Hu Y, Huang Y, Ding J, Liu Y, Fan D, Li T, et al. Status of clinical research in China. Lancet. 2011;377(9760):124–125. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60017-2. - PubMed
-
- Tong D, Wang L, Jiang J. Publications from China in The Lancet, NEJM, and JAMA. Lancet. 2013;381(9882):1983. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(13)61197-6. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous