mRNA and methylation profiling of radioresistant esophageal cancer cells: the involvement of Sall2 in acquired aggressive phenotypes
- PMID: 28367244
- PMCID: PMC5370508
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.15652
mRNA and methylation profiling of radioresistant esophageal cancer cells: the involvement of Sall2 in acquired aggressive phenotypes
Abstract
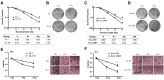
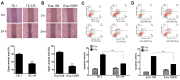
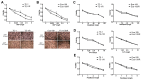
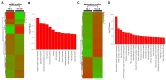
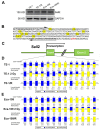
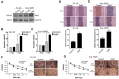
Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) is one of the deadliest malignancies worldwide. Radiotherapy plays a critical role in the curative management of inoperable ESCC patients. However, radioresistance restricts the efficacy of radiotherapy for ESCC patients. The molecules involved in radioresistance remain largely unknown, and new approaches to sensitize cells to irradiation are in demand. Technical advances in analysis of mRNA and methylation have enabled the exploration of the etiology of diseases and have the potential to broaden our understanding of the molecular pathways of ESCC radioresistance. In this study, we constructed radioresistant TE-1 and Eca-109 cell lines (TE-1/R and Eca-109/R, respectively). The radioresistant cells showed an increased migration ability but reduced apoptosis and cisplatin sensitivity compared with their parent cells. mRNA and methylation profiling by microarray revealed 1192 preferentially expressed mRNAs and 8841 aberrantly methylated regions between TE-1/R and TE-1 cells. By integrating the mRNA and methylation profiles, we related the decreased expression of transcription factor Sall2 with a corresponding increase in its methylation in TE-1/R cells, indicating its involvement in radioresistance. Upregulation of Sall2 decreased the growth and migration advantage of radioresistant ESCC cells. Taken together, our present findings illustrate the mRNA and DNA methylation changes during the radioresistance of ESCC and the important role of Sall2 in esophageal cancer malignancy.
Keywords: Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC); promoter methylation, Sall2; radioresistance.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:5–29. - PubMed
-
- Enzinger PC, Mayer RJ. Esophageal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2003;349:2241–52. - PubMed
-
- Chen H, Wu Z, Chen J, Lin X, Zheng C, Fan Y. et al. Postoperative adjuvant therapy for resectable thoracic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: a retrospective analysis of 426 cases. Med Oncol. 2015;32:417. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

