Intraoperative monitoring of flash visual evoked potential under general anesthesia
- PMID: 28367282
- PMCID: PMC5370309
- DOI: 10.4097/kjae.2017.70.2.127
Intraoperative monitoring of flash visual evoked potential under general anesthesia
Abstract
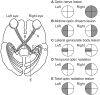
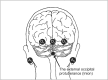
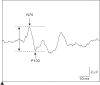
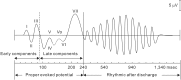
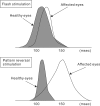
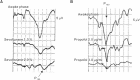
In neurosurgical procedures that may cause visual impairment in the intraoperative period, the monitoring of flash visual evoked potential (VEP) is clinically used to evaluate visual function. Patients are unconscious during surgery under general anesthesia, making flash VEP monitoring useful as it can objectively evaluate visual function. The flash stimulus input to the retina is transmitted to the optic nerve, optic chiasm, optic tract, lateral geniculate body, optic radiation (geniculocalcarine tract), and visual cortical area, and the VEP waveform is recorded from the occipital region. Intraoperative flash VEP monitoring allows detection of dysfunction arising anywhere in the optic pathway, from the retina to the visual cortex. Particularly important steps to obtain reproducible intraoperative flash VEP waveforms under general anesthesia are total intravenous anesthesia with propofol, use of retinal flash stimulation devices using high-intensity light-emitting diodes, and a combination of electroretinography to confirm that the flash stimulus has reached the retina. Relatively major postoperative visual impairment can be detected by intraoperative decreases in the flash VEP amplitude.
Keywords: Flash stimulation; General anesthesia; Intraoperative monitoring; Visual evoked potential.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Intraoperative Visual Evoked Potential Monitoring].Masui. 2015 May;64(5):508-14. Masui. 2015. PMID: 26422958 Japanese.
-
Intraoperative monitoring of visual evoked potential: introduction of a clinically useful method.J Neurosurg. 2010 Feb;112(2):273-84. doi: 10.3171/2008.9.JNS08451. J Neurosurg. 2010. PMID: 19199497
-
[Intraoperative monitoring of visual evoked potentials].Masui. 2006 Mar;55(3):302-13. Masui. 2006. PMID: 16541779 Japanese.
-
[Continuous monitoring of cortical visual evoked potentials by means of subdural electrodes in surgery on the posterior optic pathway. A case report and review of the literature].Rev Neurol. 2012 Sep 16;55(6):343-8. Rev Neurol. 2012. PMID: 22972576 Review. Spanish.
-
Visually evoked potentials and electroretinography in neurologic evaluation.Neurol Clin. 1991 Feb;9(1):225-42. Neurol Clin. 1991. PMID: 1849226 Review.
Cited by
-
Intraoperative monitoring of visual evoked potentials in patients undergoing transsphenoidal surgery for pituitary adenoma: a systematic review.BMC Neurol. 2021 Jul 23;21(1):287. doi: 10.1186/s12883-021-02315-4. BMC Neurol. 2021. PMID: 34301198 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of desflurane anesthesia on flash visual evoked potential monitoring in patients undergoing spine surgery: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2024 Jun 6;25(1):362. doi: 10.1186/s13063-024-08211-9. Trials. 2024. PMID: 38840210 Free PMC article.
-
Postoperative Improvement of Visual Function Following Amplitude Increase in Intraoperative Off-Response Visual Evoked Potential (VEP) Monitoring During a Skull Base Meningioma Surgery.Cureus. 2025 Apr 19;17(4):e82563. doi: 10.7759/cureus.82563. eCollection 2025 Apr. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40390717 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution of flash visual evoked potentials to monitor visual pathway integrity during tumor resection: illustrative cases and literature review.Neurosurg Rev. 2023 Jan 30;46(1):46. doi: 10.1007/s10143-023-01955-z. Neurosurg Rev. 2023. PMID: 36715828 Review.
-
A novel system for measuring visual potentials evoked by passive head-mounted display stimulators.Doc Ophthalmol. 2022 Apr;144(2):125-135. doi: 10.1007/s10633-021-09856-6. Epub 2021 Oct 18. Doc Ophthalmol. 2022. PMID: 34661850
References
-
- Wright JE, Arden G, Jones BR. Continuous monitoring of the visually evoked response during intra-orbital surgery. Trans Ophthalmol Soc U K. 1973;93:311–314. - PubMed
-
- Cedzich C, Schramm J. Monitoring of flash visual evoked potentials during neurosurgical operations. Int Anesthesiol Clin. 1990;28:165–169. - PubMed
-
- Neuloh G. Time to revisit VEP monitoring? Acta Neurochir (Wien) 2010;152:649–650. - PubMed
-
- Sasaki T, Itakura T, Suzuki K, Kasuya H, Munakata R, Muramatsu H, et al. Intraoperative monitoring of visual evoked potential: introduction of a clinically useful method. J Neurosurg. 2010;112:273–284. - PubMed
-
- Kodama K, Goto T, Sato A, Sakai K, Tanaka Y, Hongo K. Standard and limitation of intraoperative monitoring of the visual evoked potential. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 2010;152:643–648. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

