Learning curves for three specific procedures by anesthesiology residents using the learning curve cumulative sum (LC-CUSUM) test
- PMID: 28367291
- PMCID: PMC5370306
- DOI: 10.4097/kjae.2017.70.2.196
Learning curves for three specific procedures by anesthesiology residents using the learning curve cumulative sum (LC-CUSUM) test
Abstract
Background: The learning curve cumulative sum (LC-CUSUM) test is an innovative tool that allows quantitative monitoring of individual medical performance during the learning process by determining when a predefined acceptable level of performance is reached. This study used the LC-CUSUM test to monitor the learning process and failure rate of anesthesia residents training for specific subspecialty anesthesia procedures.
Methods: The study included 490 tracheal punctures (TP) for jet ventilation, 340 thoracic epidural analgesia (TEA) procedures, and 246 fiberoptic nasal intubations (FONI) performed by 18 residents during their single 6-month rotation.
Results: Overall, 27 (14-52), 19 (5-41), and 14 (6-33) TP, TEA, and FONI procedures were performed, respectively, by each resident. In total, 2 of 18 residents achieved an acceptable failure rate for TEA according to the literature and 4 of 18 achieved an acceptable failure rate for FONI, while none of the residents attained an acceptable rate for TP.
Conclusions: A single 6-month rotation in a reference teaching center may not be sufficient to train residents to perform specific or sub-specialty procedures as required. A regional learning network may be useful. More patient-based data are necessary to conduct a risk adjustment analysis for such specific procedures.
Keywords: Anesthesiology residency; Cumulative sum; Epidural; Intubation; Learning curve; Tracheal puncture.
Figures


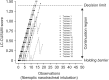
References
-
- Lim TO, Soraya A, Ding LM, Morad Z. Assessing doctors' competence: application of CUSUM technique in monitoring doctors' perfor mance. Int J Qual Health Care. 2002;14:251–258. - PubMed
-
- Biau DJ, Porcher R. A method for monitoring a process from an out of control to an in control state: Application to the learning curve. Stat Med. 2010;29:1900–1909. - PubMed
-
- Biau DJ, Williams SM, Schlup MM, Nizard RS, Porcher R. Quantitative and individualized assessment of the learning curve using LC-CUSUM. Br J Surg. 2008;95:925–929. - PubMed
-
- de Leval MR, François K, Bull C, Brawn W, Spiegelhalter D. Analysis of a cluster of surgical failures. Application to a series of neonatal arterial switch operations. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1994;107:914–923. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

