Thoracic interfascial nerve block for breast surgery in a pregnant woman: a case report
- PMID: 28367293
- PMCID: PMC5370295
- DOI: 10.4097/kjae.2017.70.2.209
Thoracic interfascial nerve block for breast surgery in a pregnant woman: a case report
Abstract
Regional anesthesia for non-obstetric surgery in parturients is a method to decrease patient and fetal risk during general anesthesia. Thoracic interfascial nerve block can be used as an analgesic technique for surgical procedures of the thorax. The Pecs II block is an interfascial block that targets not only the medial and lateral pectoral nerves, but also the lateral cutaneous branch of the intercostal nerve. Pecto-intercostal fascial block (PIFB) targets the anterior cutaneous branch of the intercostal nerve. The authors successfully performed a modified Pecs II block and PIFB without complications in a parturient who refused general anesthesia for breast surgery.
Keywords: Breast surgery; Parturient; Regional anesthesia.
Figures
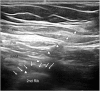
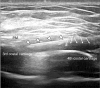
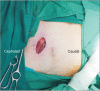
References
-
- Melnick DM, Wahl WL, Dalton VK. Management of general surgical problems in the pregnant patient. Am J Surg. 2004;187:170–180. - PubMed
-
- Heesen M, Klimek M. Nonobstetric anesthesia during pregnancy. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2016;29:297–303. - PubMed
-
- Flood P. Fetal anesthesia and brain development. Anesthesiology. 2011;114:479–480. - PubMed
-
- Van De Velde M, De Buck F. Anesthesia for non-obstetric surgery in the pregnant patient. Minerva Anestesiol. 2007;73:235–240. - PubMed
-
- Blanco R. The ‘pecs block’: a novel technique for providing analgesia after breast surgery. Anaesthesia. 2011;66:847–848. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

