Analysis of Early Neurovascular Complications of Pediatric Supracondylar Humerus Fractures: A Long-Term Observation
- PMID: 28367440
- PMCID: PMC5359433
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/2803790
Analysis of Early Neurovascular Complications of Pediatric Supracondylar Humerus Fractures: A Long-Term Observation
Abstract
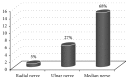
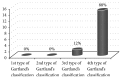
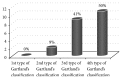
Purpose. Analysis of early vascular and nerve complications of supracondylar humerus fractures in children. Material and Methods. 220 children hospitalized in the Pediatric Trauma-Orthopedic Department in the years 2004-2014. The group consisted of 143 males and 77 females. Results. Acute neurovascular complications occurred in 16.81% of patients with displaced supracondylar fracture (37 children). Nerve damage was found in 10% of patients with displaced fracture (22 children). The most injured nerve was median nerve; this complication occurred in 15 patients (68.18%). The total nerve function returned after average of 122 days (0-220 days after surgery). Symptoms of vascular injury occurred in 7.7% children with displaced fracture (17 children). Conclusions. (1) In children with supracondylar fracture the most often injured nerve is median nerve. (2) The incidence of vascular and nerve complications positively correlates with the progression of fracture according to Gartland classification.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest were declared by the authors.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical