Brief communication: MRGPRX2, atopic dermatitis and red man syndrome
- PMID: 28367504
- PMCID: PMC5375112
- DOI: 10.1097/itx.0000000000000005
Brief communication: MRGPRX2, atopic dermatitis and red man syndrome
Abstract
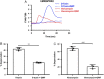
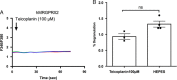
Vancoymycin causes red man syndrome, an itchy erythematous eruption involving the face, neck and upper torso. Atopic dermatitis also manifests itch and erythema, and staphylococcus δ-toxin contributes to this process. The antibiotic and toxin each provoke mast cell degranulation but the mechanism had not been understood. We have determined that these compounds evoke degranulation via interaction with the same receptor, MRGPRX2, on mast cells. A receptor antagonist inhibits this process. Antagonists of this receptor may have therapeutic potential.
Figures
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
