Vitamin D Reduces Oxidative Stress-Induced Procaspase-3/ROCK1 Activation and MP Release by Placental Trophoblasts
- PMID: 28368445
- PMCID: PMC5470774
- DOI: 10.1210/jc.2016-3753
Vitamin D Reduces Oxidative Stress-Induced Procaspase-3/ROCK1 Activation and MP Release by Placental Trophoblasts
Abstract
Context: Increased microparticle (MP) shedding by placental trophoblasts contributes to maternal vascular inflammatory response and endothelial dysfunction in preeclampsia. Vitamin D has beneficial effects in pregnancy; however, its effect on trophoblast MP release has not been investigated.
Objective: To investigate if vitamin D could protect trophoblasts from oxidative stress-induced MP release.
Design: Placental trophoblasts were isolated from uncomplicated and preeclamptic placentas. Effects of vitamin D on MP release induced by oxidative stress inducer CoCl2 were studied.
Main outcome measures: Annexin V+ MPs were assessed by flow cytometry. Expression of caveolin-1, endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS), procaspase-3, cleaved caspase-3, and Rho-associated coiled-coil protein kinase 1 (ROCK1) in trophoblasts and trophoblast-derived MPs were determined by Western blot.
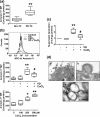
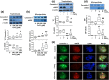
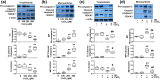
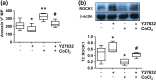
Results: Trophoblasts from preeclamptic pregnancies released significantly more MPs than cells from uncomplicated pregnancies (P < 0.01). CoCl2-induced increase in MP release was associated with upregulation of caveolin-1 and downregulation of eNOS expression in trophoblasts (P < 0.05), which could be attenuated by 1,25(OH)2D3. Moreover, 1,25(OH)2D3 could also inhibit CoCl2-induced procaspase-3 cleavage and ROCK1 activation in trophoblasts. Consistently, CoCl2-induced upregulation of procaspase-3, cleaved caspase-3, and ROCK1 expression in trophoblast-derived MPs were also reduced in cells treated with 1,25(OH)2D3.
Conclusions: Placental trophoblasts from preeclamptic pregnancies released more MP than cells from uncomplicated pregnancies. Oxidative stress-induced increase in MP shedding is associated with upregulation of caveolin-1 and downregulation of eNOS expression in placental trophoblasts. Inhibition of caspase-3 cleavage and ROCK1 activation, together with upregulation of eNOS expression, could be the potential cellular/molecular mechanism(s) of vitamin D protective effects on placental trophoblasts.
Copyright © 2017 Endocrine Society
Figures
References
-
- Knight M, Redman CWG, Linton EA, Sargent IL. Shedding of syncytiotrophoblast microvilli into the maternal circulation in pre-eclamptic pregnancies. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1998;105(6):632–640. - PubMed
-
- Burton GJ, Jones CJ. Syncytial knots, sprouts, apoptosis, and trophoblast deportation from the human placenta. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol. 2009;48(1):28–37. - PubMed
-
- Redman CW, Sargent IL. Circulating microparticles in normal pregnancy and pre-eclampsia. Placenta. 2008;29(Suppl A):S73–S77. - PubMed
-
- Goswami D, Tannetta DS, Magee LA, Fuchisawa A, Redman CW, Sargent IL, von Dadelszen P. Excess syncytiotrophoblast microparticle shedding is a feature of early-onset pre-eclampsia, but not normotensive intrauterine growth restriction. Placenta. 2006;27(1):56–61. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

