Siglec-8 and Siglec-9 binding specificities and endogenous airway ligand distributions and properties
- PMID: 28369504
- PMCID: PMC5458540
- DOI: 10.1093/glycob/cwx026
Siglec-8 and Siglec-9 binding specificities and endogenous airway ligand distributions and properties
Abstract
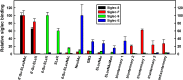
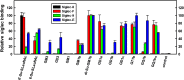
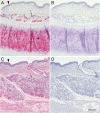
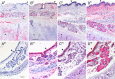
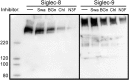
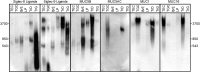
Siglecs are transmembrane sialoglycan binding proteins, most of which are expressed on leukocyte subsets and have inhibitory motifs that translate cell surface ligation into immune suppression. In humans, Siglec-8 on eosinophils, mast cells and basophils and Siglec-9 on neutrophils, monocytes and some T-cells, mediate immune cell death, inhibition of immune mediator release and/or enhancement of anti-inflammatory mediator release. Endogenous sialoglycan ligands in tissues, mostly uncharacterized, engage siglecs on leukocytes to inhibit inflammation. Glycan array analyses demonstrated that Siglec-8, Siglec-9 and their mouse counterparts Siglec-F and Siglec-E (respectively) have distinct glycan binding specificities, with Siglec-8 more structurally restricted. Since siglecs are involved in lung inflammation, we studied Siglec-8 and Siglec-9 ligands in human lungs and airways. Siglec-8 ligands are in tracheal submucosal glands and cartilage but not airway epithelium or connective tissues, whereas Siglec-9 ligands are broadly distributed. Mouse airways do not have Siglec-8 ligands, whereas Siglec-9 ligands are on airways of both species. Extraction of human airways and lung followed by electrophoretic resolution and siglec blotting revealed Siglec-8 ligands in extracts of human trachea and cultured tracheal gland cells, but not parenchyma or cultured airway epithelial cells whereas Siglec-9 ligands were extracted from all airway and lung tissues and cells tested. Siglec-8 and Siglec-9 ligands in airways appear to be high molecular weight O-linked sialoglycoproteins. These data reveal differential glycan specificities of Siglec-8, Siglec-9 and their mouse counterparts Siglec-F and Siglec-E, and the tissue distributions and molecular characteristics of Siglec-8 and Siglec-9 sialoglycan ligands on human airways and lungs.
Keywords: airways; sialic acid; siglec; submucosal glands; trachea.
© The Author 2017. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sialylated keratan sulfate proteoglycans are Siglec-8 ligands in human airways.Glycobiology. 2018 Oct 1;28(10):786-801. doi: 10.1093/glycob/cwy057. Glycobiology. 2018. PMID: 29924315 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of ligands for Siglec-8 and Siglec-9 in human airways and airway cells.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015 Mar;135(3):799-810.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2015.01.004. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25747723 Free PMC article.
-
Siglec-8 on human eosinophils and mast cells, and Siglec-F on murine eosinophils, are functionally related inhibitory receptors.Clin Exp Allergy. 2009 Mar;39(3):317-24. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2008.03173.x. Clin Exp Allergy. 2009. PMID: 19178537 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Studies on the Detection, Expression, Glycosylation, Dimerization, and Ligand Binding Properties of Mouse Siglec-E.J Biol Chem. 2017 Jan 20;292(3):1029-1037. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.738351. Epub 2016 Dec 5. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 27920204 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of airway inflammation by Siglec-8 and Siglec-9 sialoglycan ligand expression.Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016 Feb;16(1):24-30. doi: 10.1097/ACI.0000000000000234. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26694037 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Novel Blood-Derived Extracellular Vesicle-Based Biomarkers in Alzheimer's Disease Identified by Proximity Extension Assay.Biomedicines. 2020 Jul 7;8(7):199. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines8070199. Biomedicines. 2020. PMID: 32645971 Free PMC article.
-
Complementary Role of GlcNAc6ST2 and GlcNAc6ST3 in Synthesis of CL40-Reactive Sialylated and Sulfated Glycans in the Mouse Pleural Mesothelium.Molecules. 2022 Jul 16;27(14):4543. doi: 10.3390/molecules27144543. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35889417 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor-associated O-glycans of MUC1: Carriers of the glyco-code and targets for cancer vaccine design.Semin Immunol. 2020 Feb;47:101389. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2020.101389. Epub 2020 Jan 9. Semin Immunol. 2020. PMID: 31926647 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent progress in targeting the sialylated glycan-SIGLEC axis in cancer immunotherapy.Cancer Biol Med. 2023 May 3;20(5):369-84. doi: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2023.0046. Cancer Biol Med. 2023. PMID: 37133224 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-like lectin 9 as a potential therapeutic target for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Chin Med J (Engl). 2021 Feb 16;134(7):757-764. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000001381. Chin Med J (Engl). 2021. PMID: 33595976 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

