Tick-Borne Zoonoses in the United States: Persistent and Emerging Threats to Human Health
- PMID: 28369515
- PMCID: PMC5610605
- DOI: 10.1093/ilar/ilx005
Tick-Borne Zoonoses in the United States: Persistent and Emerging Threats to Human Health
Abstract
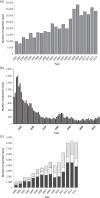
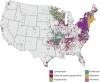
In the United States, ticks transmit the greatest diversity of arthropod-borne pathogens and are responsible for the most cases of all vector-borne diseases. In recent decades, the number of reported cases of notifiable tick-borne diseases has steadily increased, geographic distributions of many ticks and tick-borne diseases have expanded, and new tick-borne disease agents have been recognized. In this review, we (1) describe the known disease agents associated with the most commonly human-biting ixodid ticks, (2) review the natural histories of these ticks and their associated pathogens, (3) highlight spatial and temporal changes in vector tick distributions and tick-borne disease occurrence in recent decades, and (4) identify knowledge gaps and barriers to more effective prevention of tick-borne diseases. We describe 12 major tick-borne diseases caused by 15 distinct disease agents that are transmitted by the 8 most commonly human-biting ixodid ticks in the United States. Notably, 40% of these pathogens were described within the last two decades. Our assessment highlights the importance of animal studies to elucidate how tick-borne pathogens are maintained in nature, as well as advances in molecular detection of pathogens which has led to the discovery of several new tick-borne disease agents.
Figures

References
-
- Adams DA, Thomas KR, Jajosky R, Sharp P, Onweh D, Schley A, Anderson W, Faulkner A, Kugeler K. Summary of notifiable infectious disease conditions—United States, 2014. Morbid Mortal Wkly Rep. 2016;63:1–52. - PubMed
-
- Anziani OS, Ewing SA, Barker RW. Experimental transmission of a granulocytic form of the tribe Ehrlichieae by Dermacentor variabilis and Amblyomma americanum to dogs. Am J Vet Res. 1990;51(6):929–931. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

