Involvement of reactive oxygen species in ionizing radiation-induced upregulation of cell surface Toll-like receptor 2 and 4 expression in human monocytic cells
- PMID: 28369600
- PMCID: PMC5737079
- DOI: 10.1093/jrr/rrx011
Involvement of reactive oxygen species in ionizing radiation-induced upregulation of cell surface Toll-like receptor 2 and 4 expression in human monocytic cells
Abstract
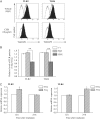
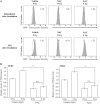
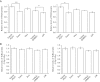
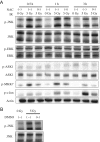
Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are pattern recognition receptors that recognize pathogen-associated molecular patterns and are indispensable for antibacterial and antiviral immunity. Our previous report showed that ionizing radiation increases the cell surface expressions of TLR2 and TLR4 and enhances their responses to agonists in human monocytic THP1 cells. The present study investigated how ionizing radiation increases the cell surface expressions of TLR2 and TLR4 in THP1 cells. The THP1 cells treated or not treated with pharmaceutical agents such as cycloheximide and N-acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC) were exposed to X-ray irradiation, following which the expressions of TLRs and mitogen-activated protein kinase were analyzed. X-ray irradiation increased the mRNA expressions of TLR2 and TLR4, and treatment with a protein synthesis inhibitor cycloheximide abolished the radiation-induced upregulation of their cell surface expressions. These results indicate that radiation increased those receptors through de novo protein synthesis. Furthermore, treatment with an antioxidant NAC suppressed not only the radiation-induced upregulation of cell surface expressions of TLR2 and TLR4, but also the radiation-induced activation of the c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) pathway. Since it has been shown that the inhibitor for JNK can suppress the radiation-induced upregulation of TLR expression, the present results suggest that ionizing radiation increased the cell surface expressions of TLR2 and TLR4 through reactive oxygen species-mediated JNK activation.
Keywords: Toll-like receptor; c-Jun N-terminal kinase; ionizing radiation; reactive oxygen species.
© The Author 2017. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of The Japan Radiation Research Society and Japanese Society for Radiation Oncology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ionizing radiation affects the expression of Toll-like receptors 2 and 4 in human monocytic cells through c-Jun N-terminal kinase activation.J Radiat Res. 2014 Sep;55(5):876-84. doi: 10.1093/jrr/rru040. Epub 2014 Jun 13. J Radiat Res. 2014. PMID: 24927726 Free PMC article.
-
Female sex hormones modulate Porphyromonas gingivalis lipopolysaccharide-induced Toll-like receptor signaling in primary human monocytes.J Periodontal Res. 2016 Jun;51(3):395-406. doi: 10.1111/jre.12320. Epub 2015 Sep 14. J Periodontal Res. 2016. PMID: 26364725
-
The role of Toll-like receptor 4 in high-glucose-induced inflammatory and fibrosis markers in human peritoneal mesothelial cells.Int Urol Nephrol. 2017 Jan;49(1):171-181. doi: 10.1007/s11255-016-1430-9. Epub 2016 Oct 8. Int Urol Nephrol. 2017. PMID: 27722989
-
Role of the Toll Like receptor (TLR) radical cycle in chronic inflammation: possible treatments targeting the TLR4 pathway.Mol Neurobiol. 2013 Aug;48(1):190-204. doi: 10.1007/s12035-013-8425-7. Epub 2013 Feb 26. Mol Neurobiol. 2013. PMID: 23436141 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ionizing radiation and toll like receptors: A systematic review article.Hum Immunol. 2021 Jun;82(6):446-454. doi: 10.1016/j.humimm.2021.03.008. Epub 2021 Mar 31. Hum Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33812705
Cited by
-
Effects and Related Mechanisms of the Senolytic Agent ABT-263 on the Survival of Irradiated A549 and Ca9-22 Cancer Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 8;22(24):13233. doi: 10.3390/ijms222413233. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34948029 Free PMC article.
-
DAP3 Is Involved in Modulation of Cellular Radiation Response by RIG-I-Like Receptor Agonist in Human Lung Adenocarcinoma Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 3;22(1):420. doi: 10.3390/ijms22010420. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33401559 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of homologous recombination in response to ionizing radiation-induced DNA damage.Int J Radiat Biol. 2023;99(6):903-914. doi: 10.1080/09553002.2021.1956001. Epub 2021 Aug 4. Int J Radiat Biol. 2023. PMID: 34283012 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emodin Inhibition of Influenza A Virus Replication and Influenza Viral Pneumonia via the Nrf2, TLR4, p38/JNK and NF-kappaB Pathways.Molecules. 2017 Oct 18;22(10):1754. doi: 10.3390/molecules22101754. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 29057806 Free PMC article.
-
A comprehensive review of sensors of radiation-induced damage, radiation-induced proximal events, and cell death.Immunol Rev. 2025 Jan;329(1):e13409. doi: 10.1111/imr.13409. Epub 2024 Oct 19. Immunol Rev. 2025. PMID: 39425547 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

