Structure of the Y. pseudotuberculosis adhesin InvasinE
- PMID: 28370712
- PMCID: PMC5441405
- DOI: 10.1002/pro.3171
Structure of the Y. pseudotuberculosis adhesin InvasinE
Abstract
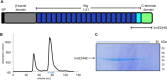
Enteropathogenic Yersinia expresses several invasins that are fundamental virulence factors required for adherence and colonization of tissues in the host. Within the invasin-family of Yersinia adhesins, to date only Invasin has been extensively studied at both structural and functional levels. In this work, we structurally characterize the recently identified inverse autotransporter InvasinE from Yersinia pseudotuberculosis (formerly InvasinD from Yersinia pseudotuberculosis strain IP31758) that belongs to the invasin-family of proteins. The sequence of the C-terminal adhesion domain of InvasinE differs significantly from that of other members of the Yersinia invasin-family and its detailed cellular and molecular function remains elusive. In this work, we present the 1.7 Å crystal structure of the adhesion domain of InvasinE along with two Immunoglobulin-like domains. The structure reveals a rod shaped architecture, confirmed by small angle X-ray scattering in solution. The adhesion domain exhibits strong structural similarities to the C-type lectin-like domain of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis Invasin and enteropathogenic/enterohemorrhagic E. coli Intimin. However, despite the overall structural similarity, the C-type lectin-like domain in InvasinE lacks motifs required for Ca2+ /carbohydrate binding as well as sequence or structural features critical for Tir binding in Intimin and β1 -integrin binding in Invasin, suggesting that InvasinE targets a distinct, yet unidentified molecule on the host-cell surface. Although the biological role and target molecule of InvasinE remain to be elucidated, our structural data provide novel insights into the architecture of invasin-family proteins and a platform for further studies towards unraveling the function of InvasinE in the context of infection and host colonization.
Keywords: C-type lectin-like domain; X-ray crystallography; Yersinia; adhesion; invasion; small angle X-ray scattering.
© 2017 The Protein Society.
Figures






References
-
- Bottone EJ (1999) Yersinia enterocolitica: overview and epidemiologic correlates. Microbes Infect 1:323–333. - PubMed
-
- Isberg RR, Voorhis DL, Falkow S (1987) Identification of invasin: a protein that allows enteric bacteria to penetrate cultured mammalian cells. Cell 50:769–778. - PubMed
-
- Chauhan N, Wrobel A, Skurnik M, Leo JC (2016) Yersinia adhesins: an arsenal for infection. Proteomics Clin Appl. 10:949–963. - PubMed
-
- Leo JC, Oberhettinger P, Schütz M, Linke D (2015) The inverse autotransporter family: intimin, invasin and related proteins. Int J Med Microbiol 305:276–282. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

