Impact of ibrutinib dose adherence on therapeutic efficacy in patients with previously treated CLL/SLL
- PMID: 28373262
- PMCID: PMC5437732
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2016-12-737346
Impact of ibrutinib dose adherence on therapeutic efficacy in patients with previously treated CLL/SLL
Abstract
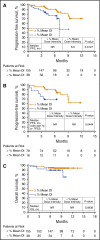
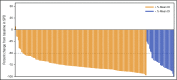
Ibrutinib, an oral inhibitor of Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK), at a once-daily dose of 420 mg achieved BTK active-site occupancy in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)/small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL) that was maintained at 24 hours. It is unknown if intermittent interruption of ibrutinib therapy contributes to altered clinical outcomes. We therefore evaluated the effect of ibrutinib dose adherence on patient outcomes in the phase 3 RESONATE trial. The overall mean dose intensity (DI) was 95% with median treatment duration of ∼9 months. Pharmacokinetic assessment of ibrutinib exposure at 420-mg dose suggested similar exposure regardless of patient weight or age. As assessed by independent review committee, patients with higher DI experienced longer median progression-free survival (PFS) compared with those with lower DI regardless of del17p and/or TP53 status. Of 79 patients requiring a drug hold, treatment was restarted at the original dose in 73 (92%) patients. Mean duration of a missed-dose event was 18.7 days (range, 8-56). Patients missing ≥8 consecutive days of ibrutinib had a shorter median PFS vs those missing <8 days (10.9 months vs not reached). These results support sustained adherence to once-daily ibrutinib dosing at 420 mg as clinically feasible to achieve optimal outcomes in patients with previously treated CLL. The trial was registered at www.clinicaltrials.gov as #NCT01578707.
© 2017 by The American Society of Hematology.
Figures
References
-
- Rai KR, Peterson BL, Appelbaum FR, et al. . Fludarabine compared with chlorambucil as primary therapy for chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2000;343(24):1750-1757. - PubMed
-
- Goede V, Fischer K, Busch R, et al. . Obinutuzumab plus chlorambucil in patients with CLL and coexisting conditions. N Engl J Med. 2014;370(12):1101-1110. - PubMed
-
- Hallek M, Fischer K, Fingerle-Rowson G, et al. ; International Group of Investigators; German Chronic Lymphocytic Leukaemia Study Group. Addition of rituximab to fludarabine and cyclophosphamide in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: a randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2010;376(9747):1164-1174. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

