Polycystic Kidney Disease with Hyperinsulinemic Hypoglycemia Caused by a Promoter Mutation in Phosphomannomutase 2
- PMID: 28373276
- PMCID: PMC5533241
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2016121312
Polycystic Kidney Disease with Hyperinsulinemic Hypoglycemia Caused by a Promoter Mutation in Phosphomannomutase 2
Abstract
Hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia (HI) and congenital polycystic kidney disease (PKD) are rare, genetically heterogeneous disorders. The co-occurrence of these disorders (HIPKD) in 17 children from 11 unrelated families suggested an unrecognized genetic disorder. Whole-genome linkage analysis in five informative families identified a single significant locus on chromosome 16p13.2 (logarithm of odds score 6.5). Sequencing of the coding regions of all linked genes failed to identify biallelic mutations. Instead, we found in all patients a promoter mutation (c.-167G>T) in the phosphomannomutase 2 gene (PMM2), either homozygous or in trans with PMM2 coding mutations. PMM2 encodes a key enzyme in N-glycosylation. Abnormal glycosylation has been associated with PKD, and we found that deglycosylation in cultured pancreatic β cells altered insulin secretion. Recessive coding mutations in PMM2 cause congenital disorder of glycosylation type 1a (CDG1A), a devastating multisystem disorder with prominent neurologic involvement. Yet our patients did not exhibit the typical clinical or diagnostic features of CDG1A. In vitro, the PMM2 promoter mutation associated with decreased transcriptional activity in patient kidney cells and impaired binding of the transcription factor ZNF143. In silico analysis suggested an important role of ZNF143 for the formation of a chromatin loop including PMM2 We propose that the PMM2 promoter mutation alters tissue-specific chromatin loop formation, with consequent organ-specific deficiency of PMM2 leading to the restricted phenotype of HIPKD. Our findings extend the spectrum of genetic causes for both HI and PKD and provide insights into gene regulation and PMM2 pleiotropy.
Keywords: PMM2; ZNF143; glycosylation; hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia; polycystic kidney disease; promoter.
Copyright © 2017 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures
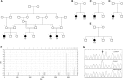
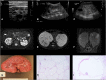
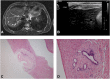
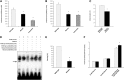
Comment in
-
Polycystic kidney disease: PMM2 mutation causes PKD and hyperinsulinism.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2017 Jun;13(6):321. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2017.58. Epub 2017 Apr 24. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2017. PMID: 28435156 No abstract available.
References
-
- Zerres K, Mücher G, Becker J, Steinkamm C, Rudnik-Schöneborn S, Heikkilä P, Rapola J, Salonen R, Germino GG, Onuchic L, Somlo S, Avner ED, Harman LA, Stockwin JM, Guay-Woodford LM: Prenatal diagnosis of autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD): Molecular genetics, clinical experience, and fetal morphology. Am J Med Genet 76: 137–144, 1998 - PubMed
-
- Gunay-Aygun M, Parisi MA, Doherty D, Tuchman M, Tsilou E, Kleiner DE, Huizing M, Turkbey B, Choyke P, Guay-Woodford L, Heller T, Szymanska K, Johnson CA, Glass I, Gahl WA: MKS3-related ciliopathy with features of autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease, nephronophthisis, and Joubert Syndrome. J Pediatr 155: 386–392.e1, 2009 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Guay-Woodford LM, Bissler JJ, Braun MC, Bockenhauer D, Cadnapaphornchai MA, Dell KM, Kerecuk L, Liebau MC, Alonso-Peclet MH, Shneider B, Emre S, Heller T, Kamath BM, Murray KF, Moise K, Eichenwald EE, Evans J, Keller RL, Wilkins-Haug L, Bergmann C, Gunay-Aygun M, Hooper SR, Hardy KK, Hartung EA, Streisand R, Perrone R, Moxey-Mims M: Consensus expert recommendations for the diagnosis and management of autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease: Report of an international conference. J Pediatr 165: 611–617, 2014 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Flanagan SE, Kapoor RR, Hussain K: Genetics of congenital hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia. Semin Pediatr Surg 20: 13–17, 2011 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

