Arthroscopic Partial Repair of Irreparable, Massive Rotator Cuff Tears
- PMID: 28373953
- PMCID: PMC5368352
- DOI: 10.1016/j.eats.2016.09.020
Arthroscopic Partial Repair of Irreparable, Massive Rotator Cuff Tears
Abstract
Several treatment options for chronic, massive rotator cuff tears exist, and they include debridement with possible biceps tenotomy or tenodesis, open or arthroscopic partial repair, muscle or tendon transfer, superior capsule reconstruction, synthetic patch augmentation, and reverse total shoulder arthroplasty. The aim of this technique article is to describe our preferred surgical option for irreparable, massive rotator cuff tears with an irreparable supraspinatus, a reparable infraspinatus, and an intact or reparable subscapularis tendon.
Figures


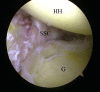
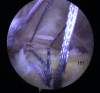
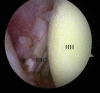
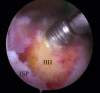

References
-
- Burkhart S.S., Nottage W.M., Ogilvie-Harris D.J., Kohn H.S., Pachelli A. Partial repair of irreparable rotator cuff tears. Arthroscopy. 1994;10:363–370. - PubMed
-
- Burkhart S.S. Arthroscopic treatment of massive rotator cuff tears. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001;(390):107–118. - PubMed
-
- Burkhart S.S., Athanasiou K.A., Wirth M.A. Margin convergence: A method of reducing strain in massive rotator cuff tears. Arthroscopy. 1996;12:335–338. - PubMed
-
- Mori D., Funakoshi N., Yamashita F. Arthroscopic surgery of irreparable large or massive rotator cuff tears with low-grade fatty degeneration of the infraspinatus: Patch autograft procedure versus partial repair procedure. Arthroscopy. 2013;29:1911–1921. - PubMed
-
- Castricini R., De Benedetto M., Familiari F. Functional status and failed rotator cuff repair predict outcomes after arthroscopic-assisted latissimus dorsi transfer for irreparable massive rotator cuff tears. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2016;25:658–665. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

