Hydrocephalus after Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment
- PMID: 28373987
- PMCID: PMC5360938
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/8584753
Hydrocephalus after Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment
Abstract
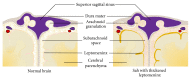
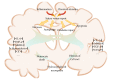
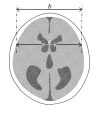
Hydrocephalus (HCP) is a common complication in patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage. In this review, we summarize the advanced research on HCP and discuss the understanding of the molecular originators of HCP and the development of diagnoses and remedies of HCP after SAH. It has been reported that inflammation, apoptosis, autophagy, and oxidative stress are the important causes of HCP, and well-known molecules including transforming growth factor, matrix metalloproteinases, and iron terminally lead to fibrosis and blockage of HCP. Potential medicines for HCP are still in preclinical status, and surgery is the most prevalent and efficient therapy, despite respective risks of different surgical methods, including lamina terminalis fenestration, ventricle-peritoneal shunting, and lumbar-peritoneal shunting. HCP remains an ailment that cannot be ignored and even with various solutions the medical community is still trying to understand and settle why and how it develops and accordingly improve the prognosis of these patients with HCP.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures


References
-
- Yamada S., Ishikawa M., Yamamoto K., Ino T., Kimura T., Kobayashi S. Aneurysm location and clipping versus coiling for development of secondary normal-pressure hydrocephalus after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: Japanese Stroke DataBank. Journal of Neurosurgery. 2015;123(6):1555–1561. doi: 10.3171/2015.1.jns142761. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

