A validation method for near-infrared spectroscopy based tissue oximeters for cerebral and somatic tissue oxygen saturation measurements
- PMID: 28374103
- PMCID: PMC5838152
- DOI: 10.1007/s10877-017-0015-1
A validation method for near-infrared spectroscopy based tissue oximeters for cerebral and somatic tissue oxygen saturation measurements
Abstract
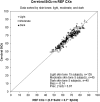
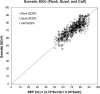
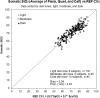
We describe the validation methodology for the NIRS based FORE-SIGHT ELITE® (CAS Medical Systems, Inc., Branford, CT, USA) tissue oximeter for cerebral and somatic tissue oxygen saturation (StO2) measurements for adult subjects submitted to the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to obtain clearance for clinical use. This validation methodology evolved from a history of NIRS validations in the literature and FDA recommended use of Deming regression and bootstrapping statistical validation methods. For cerebral validation, forehead cerebral StO2 measurements were compared to a weighted 70:30 reference (REF CXB) of co-oximeter internal jugular venous and arterial blood saturation of healthy adult subjects during a controlled hypoxia sequence, with a sensor placed on the forehead. For somatic validation, somatic StO2 measurements were compared to a weighted 70:30 reference (REF CXS) of co-oximetry central venous and arterial saturation values following a similar protocol, with sensors place on the flank, quadriceps muscle, and calf muscle. With informed consent, 25 subjects successfully completed the cerebral validation study. The bias and precision (1 SD) of cerebral StO2 compared to REF CXB was -0.14 ± 3.07%. With informed consent, 24 subjects successfully completed the somatic validation study. The bias and precision of somatic StO2 compared to REF CXS was 0.04 ± 4.22% from the average of flank, quadriceps, and calf StO2 measurements to best represent the global whole body REF CXS. The NIRS validation methods presented potentially provide a reliable means to test NIRS monitors and qualify them for clinical use.
Keywords: Cerebral oximetry; FDA; NIRS; Near Infrared Spectroscopy; Saturation; Tissue oximetry; Tissue oxygen.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
Paul Benni is an employee and owns stock in CAS Medical Systems, Inc., the manufacturer of the FORE-SIGHT Elite NIRS monitor. Paul Benni is an inventor named on several patents relating to NIRS, but has no individual royalty rights (CAS Medical Systems own rights). David MacLeod received compensation for his work on this study through Duke University. Keita Ikeda received compensation for his work on this study through Duke University. Hung-Mo Lin received consultancy fee for statistical analysis.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were approved by The Duke University Health System Institutional Review Board for Clinical Investigations (DUHS IRB). DUHS IRB complies with all U.S. regulatory requirements related to the protection of human research participants. Specifically, the DUHS IRB complies with 45CFR46, 21CFR50, 21CFR56, 21CFR312, 21CFR812, and 45CFR164.508-514. In addition, the DUHS IRB complies with the Guidelines of the International Conference on Harmonization to the extent required by the U. S. Food and Drug Administration.
Informed consent
Informed written consent was obtained from all study subjects.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Validation of a Second-Generation Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Monitor in Children With Congenital Heart Disease.Anesth Analg. 2019 Apr;128(4):661-668. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000002796. Anesth Analg. 2019. PMID: 29324491
-
The accuracy of a near-infrared spectroscopy cerebral oximetry device and its potential value for estimating jugular venous oxygen saturation.Anesth Analg. 2014 Dec;119(6):1381-92. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000000463. Anesth Analg. 2014. PMID: 25313967 Free PMC article.
-
Factors affecting the performance of 5 cerebral oximeters during hypoxia in healthy volunteers.Anesth Analg. 2013 Oct;117(4):813-823. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0b013e318297d763. Epub 2013 Sep 10. Anesth Analg. 2013. PMID: 24023027 Clinical Trial.
-
The Various Oximetric Techniques Used for the Evaluation of Blood Oxygenation.Sensors (Basel). 2020 Aug 27;20(17):4844. doi: 10.3390/s20174844. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32867184 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Near-infrared oximetry of the brain.Prog Neurobiol. 1999 Aug;58(6):541-60. doi: 10.1016/s0301-0082(98)00093-8. Prog Neurobiol. 1999. PMID: 10408656 Review.
Cited by
-
The Challenges and Pitfalls of Detecting Sleep Hypopnea Using a Wearable Optical Sensor: Comparative Study.J Med Internet Res. 2021 Jul 29;23(7):e24171. doi: 10.2196/24171. J Med Internet Res. 2021. PMID: 34326039 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative ultrasound and photoacoustic assessments of red blood cell aggregation in the human radial artery.Photoacoustics. 2025 Mar 13;43:100711. doi: 10.1016/j.pacs.2025.100711. eCollection 2025 Jun. Photoacoustics. 2025. PMID: 40165999 Free PMC article.
-
An Autonomous Implantable Device for the Prevention of Death from Opioid Overdose.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jul 2:2024.06.27.600919. doi: 10.1101/2024.06.27.600919. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Sci Adv. 2024 Oct 25;10(43):eadr3567. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adr3567. PMID: 39005313 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Recovery of organ-specific tissue oxygen delivery at restrictive transfusion thresholds after fluid treatment in ovine haemorrhagic shock.Intensive Care Med Exp. 2022 Apr 4;10(1):12. doi: 10.1186/s40635-022-00439-6. Intensive Care Med Exp. 2022. PMID: 35377109 Free PMC article.
-
Automatic photoacoustic monitoring of perinatal brain hypoxia with superior sagittal sinus detection.J Biomed Opt. 2025 Jul;30(7):076004. doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.30.7.076004. Epub 2025 Jul 11. J Biomed Opt. 2025. PMID: 40655941 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pollard V, Prough DS, DeMelo AE, Deyo DJ, Uchida T, Stoddart HF. Validation in volunteers of a near-infrared spectroscope for monitoring brain oxygenation in vivo. Anesth Analg. 1996;82(2):269–277. - PubMed
-
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) 510(k) Database http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfpmn/pmn.cfm?ID=K960614.
-
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) 510(k) Database http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfpmn/pmn.cfm?ID=K971628.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

