Rules and mechanisms for efficient two-stage learning in neural circuits
- PMID: 28374674
- PMCID: PMC5380437
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.20944
Rules and mechanisms for efficient two-stage learning in neural circuits
Abstract
Trial-and-error learning requires evaluating variable actions and reinforcing successful variants. In songbirds, vocal exploration is induced by LMAN, the output of a basal ganglia-related circuit that also contributes a corrective bias to the vocal output. This bias is gradually consolidated in RA, a motor cortex analogue downstream of LMAN. We develop a new model of such two-stage learning. Using stochastic gradient descent, we derive how the activity in 'tutor' circuits (e.g., LMAN) should match plasticity mechanisms in 'student' circuits (e.g., RA) to achieve efficient learning. We further describe a reinforcement learning framework through which the tutor can build its teaching signal. We show that mismatches between the tutor signal and the plasticity mechanism can impair learning. Applied to birdsong, our results predict the temporal structure of the corrective bias from LMAN given a plasticity rule in RA. Our framework can be applied predictively to other paired brain areas showing two-stage learning.
Keywords: birdsong; learning theory; motor control; neuroscience; reinforcement learning; zebra finch.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures

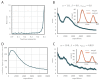
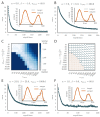
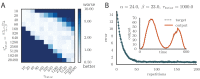

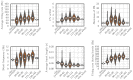
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

