640-Gbit/s fast physical random number generation using a broadband chaotic semiconductor laser
- PMID: 28374860
- PMCID: PMC5379198
- DOI: 10.1038/srep45900
640-Gbit/s fast physical random number generation using a broadband chaotic semiconductor laser
Abstract
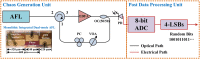
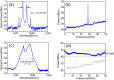
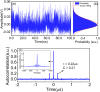
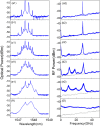
An ultra-fast physical random number generator is demonstrated utilizing a photonic integrated device based broadband chaotic source with a simple post data processing method. The compact chaotic source is implemented by using a monolithic integrated dual-mode amplified feedback laser (AFL) with self-injection, where a robust chaotic signal with RF frequency coverage of above 50 GHz and flatness of ±3.6 dB is generated. By using 4-least significant bits (LSBs) retaining from the 8-bit digitization of the chaotic waveform, random sequences with a bit-rate up to 640 Gbit/s (160 GS/s × 4 bits) are realized. The generated random bits have passed each of the fifteen NIST statistics tests (NIST SP800-22), indicating its randomness for practical applications.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


References
-
- Gallager R. G. Principles of digital communication vol. 1 (Cambridge University Press, 2008).
-
- Gisin N., Ribordy G., Tittel W. & Zbinden H. Quantum cryptography. Reviews of modern physics 74 (2002).
-
- Metropolis N. & Ulam S. The monte carlo method. Journal of the American statistical association 44 (1949). - PubMed
-
- Asmussen S. & Glynn P. W. Stochastic simulation: algorithms and analysis. Springer Science and Business Media 57 (2007).
-
- James F. A review of pseudorandom number generators. Computer Physics Communications 60 (1990).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

