Idiopathic SIADH in young patients: don't forget the nose
- PMID: 28374875
- PMCID: PMC5384315
- DOI: 10.14639/0392-100X-1141
Idiopathic SIADH in young patients: don't forget the nose
Abstract
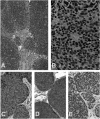
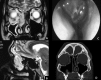
Olfactory neuroblastoma (ONB) is an uncommon neuroendocrine sinonasal cancer associated by many authors to ectopic production of several biologically active substances. We report a case of a 31-year-old male patient who presented with idiopathic syndrome of inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone (SIADH). During diagnostic work-up, a CT scan of the head was performed and an ethmoidal ONB was detected. Endoscopical surgery followed by radiotherapy was carried out. Immediately after surgery natraemia levels normalised. Five years later the patient is disease-free. To our knowledge, 17 cases of SIADH associated to ONB have been published. In nine reports, idiopathic SIADH promptly led to the diagnosis of the sinonasal mass as in our clinical case, however, in many reports, correct diagnosis was accomplished months to years later. In young patients with idiopathic inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion, a neuroendocrine malignancy of the sinonasal area must be excluded.
Il neuroblastoma olfattivo (ONB) è un raro tumore neuroendocrino dei seni paranasali associato, secondo molti autori, alla produzione di molteplici sostanze biologicamente attive. In questo lavoro descriviamo il caso di un paziente di sesso maschile di 31 anni giunto alla nostra osservazione presentando la sindrome idiopatica da inappropriata secrezione di ormone antidiuretico (SIADH). Durante il work-up diagnostico il paziente è stato sottoposto a TAC del massiccio facciale, che documentava la presenza di un estesioneuroblastoma etmoidale. è stato eseguito un trattamento di chirurgia endoscopica e successiva radioterapia. Subito dopo l’intervento chirurgico i livelli di natremia si sono normalizzati. Cinque anni più tardi il paziente risulta essere libero da malattia. Attualmente in letteratura sono stati pubblicati 17 casi di SIADH associata a ONB. In nove lavori la SIADH idiopatica ha tempestivamente portato alla diagnosi di masse sinusali come nel nostro caso, tuttavia, in molti casi, si è giunti alla diagnosi corretta mesi o anni dopo. Nei giovani pazienti con sindrome idiopatica da inappropriata secrezione di ormone antidiuretico è necessario escludere un tumore maligno neuroendocrino dei seni paranasali.
Keywords: Arginine vasopressin; Olfactory neuroblastoma; Paraneoplastic syndrome; SIADH; Sinonasal.
© Copyright by Società Italiana di Otorinolaringologia e Chirurgia Cervico-Facciale, Rome, Italy.
Figures
References
-
- Ferlito A, Rinaldo A, Devaney KO. Syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion associated with head and neck cancers: review of the literature. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1997;106(10 Pt 1):878–883. - PubMed
-
- Talmi YP, Hoffman HT, McCabe BF. Syndrome of inappropriate secretion of arginine vasopressin in patients with cancer of the head and neck. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1992;101:964–969. - PubMed
-
- Berger L, Luc R. L'esthèsioneuroèphiteliome olfactif. Bull de l'Assoc Franc pour l'Etude Cancer. 1924;13:410–420.
-
- Bouche J, Guiot G, Tessier P, et al. A further case of tumor of the olfactory placode. Sem Hop. 1967;43:587–591. - PubMed
-
- Singh W, Ramage C, Best P, et al. Nasal neuroblastoma secreting vasopressin. A case report. Cancer. 1980;45:961–966. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

