Status and methodology of publicly available national HIV care continua and 90-90-90 targets: A systematic review
- PMID: 28376085
- PMCID: PMC5380306
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1002253
Status and methodology of publicly available national HIV care continua and 90-90-90 targets: A systematic review
Abstract
Background: In 2014, the Joint United Nations Program on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) issued treatment goals for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). The 90-90-90 target specifies that by 2020, 90% of individuals living with HIV will know their HIV status, 90% of people with diagnosed HIV infection will receive antiretroviral treatment (ART), and 90% of those taking ART will be virally suppressed. Consistent methods and routine reporting in the public domain will be necessary for tracking progress towards the 90-90-90 target.
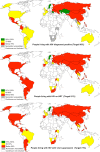
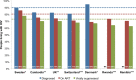
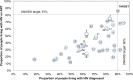
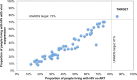
Methods and findings: For the period 2010-2016, we searched PubMed, UNAIDS country progress reports, World Health Organization (WHO), UNAIDS reports, national surveillance and program reports, United States President's Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief (PEPFAR) Country Operational Plans, and conference presentations and/or abstracts for the latest available national HIV care continuum in the public domain. Continua of care included the number and proportion of people living with HIV (PLHIV) who are diagnosed, on ART, and virally suppressed out of the estimated number of PLHIV. We ranked the described methods for indicators to derive high-, medium-, and low-quality continuum. For 2010-2016, we identified 53 national care continua with viral suppression estimates representing 19.7 million (54%) of the 2015 global estimate of PLHIV. Of the 53, 6 (with 2% of global burden) were high quality, using standard surveillance methods to derive an overall denominator and program data from national cohorts for estimating steps in the continuum. Only nine countries in sub-Saharan Africa had care continua with viral suppression estimates. Of the 53 countries, the average proportion of the aggregate of PLHIV from all countries on ART was 48%, and the proportion of PLHIV who were virally suppressed was 40%. Seven countries (Sweden, Cambodia, United Kingdom, Switzerland, Denmark, Rwanda, and Namibia) were within 12% and 10% of achieving the 90-90-90 target for "on ART" and for "viral suppression," respectively. The limitations to consider when interpreting the results include significant variation in methods used to determine national continua and the possibility that complete continua were not available through our comprehensive search of the public domain.
Conclusions: Relatively few complete national continua of care are available in the public domain, and there is considerable variation in the methods for determining progress towards the 90-90-90 target. Despite bearing the highest HIV burden, national care continua from sub-Saharan Africa were less likely to be in the public domain. A standardized monitoring and evaluation approach could improve the use of scarce resources to achieve 90-90-90 through improved transparency, accountability, and efficiency.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- United Nations News Centre. UN agencies launch programme to treat 3 million HIV-infected people by 2005. December 2003. http://www.un.org/apps/news/story.asp?NewsID=9023&Cr=hiv&Cr1=aids.
-
- Joint UN Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS). Fact Sheet 2016. Geneva, Switzerland. http://www.unaids.org/sites/default/files/media_asset/UNAIDS_FactSheet_e...
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

