Elucidation of the calcineurin-Crz1 stress response transcriptional network in the human fungal pathogen Cryptococcus neoformans
- PMID: 28376087
- PMCID: PMC5380312
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006667
Elucidation of the calcineurin-Crz1 stress response transcriptional network in the human fungal pathogen Cryptococcus neoformans
Abstract
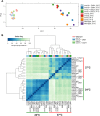
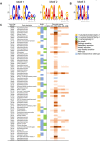
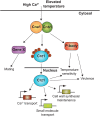
Calcineurin is a highly conserved Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent serine/threonine-specific protein phosphatase that orchestrates cellular Ca2+ signaling responses. In Cryptococcus neoformans, calcineurin is activated by multiple stresses including high temperature, and is essential for stress adaptation and virulence. The transcription factor Crz1 is a major calcineurin effector in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and other fungi. Calcineurin dephosphorylates Crz1, thereby enabling Crz1 nuclear translocation and transcription of target genes. Here we show that loss of Crz1 confers phenotypes intermediate between wild-type and calcineurin mutants, and demonstrate that deletion of the calcineurin docking domain results in the inability of Crz1 to translocate into the nucleus under thermal stress. RNA-sequencing revealed 102 genes that are regulated in a calcineurin-Crz1-dependent manner at 37°C. The majority of genes were down-regulated in cna1Δ and crz1Δ mutants, indicating these genes are normally activated by the calcineurin-Crz1 pathway at high temperature. About 58% of calcineurin-Crz1 target genes have unknown functions, while genes with known or predicted functions are involved in cell wall remodeling, calcium transport, and pheromone production. We identified three calcineurin-dependent response element motifs within the promoter regions of calcineurin-Crz1 target genes, and show that Crz1 binding to target gene promoters is increased upon thermal stress in a calcineurin-dependent fashion. Additionally, we found a large set of genes independently regulated by calcineurin, and Crz1 regulates 59 genes independently of calcineurin. Given the intermediate crz1Δ mutant phenotype, and our recent evidence for a calcineurin regulatory network impacting mRNA in P-bodies and stress granules independently of Crz1, calcineurin likely acts on factors beyond Crz1 that govern mRNA expression/stability to operate a branched transcriptional/post-transcriptional stress response network necessary for fungal virulence. Taken together, our findings reveal the core calcineurin-Crz1 stress response cascade is maintained from ascomycetes to a pathogenic basidiomycete fungus, but its output in C. neoformans appears to be adapted to promote fungal virulence.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interest exist.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Calcium Binding Protein Ncs1 Is Calcineurin Regulated in Cryptococcus neoformans and Essential for Cell Division and Virulence.mSphere. 2020 Sep 9;5(5):e00761-20. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00761-20. mSphere. 2020. PMID: 32907953 Free PMC article.
-
Calcineurin Targets Involved in Stress Survival and Fungal Virulence.PLoS Pathog. 2016 Sep 9;12(9):e1005873. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005873. eCollection 2016 Sep. PLoS Pathog. 2016. PMID: 27611567 Free PMC article.
-
The Crz1/Sp1 transcription factor of Cryptococcus neoformans is activated by calcineurin and regulates cell wall integrity.PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e51403. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0051403. Epub 2012 Dec 12. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23251520 Free PMC article.
-
CRZ1 transcription factor is involved in cell survival, stress tolerance, and virulence in fungi.J Biosci. 2022;47:66. J Biosci. 2022. PMID: 36408540 Review.
-
Coping with stress: calmodulin and calcineurin in model and pathogenic fungi.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003 Nov 28;311(4):1151-7. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(03)01528-6. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003. PMID: 14623301 Review.
Cited by
-
Multifactorial Mechanisms of Tolerance to Ketoconazole in Candida albicans.Microbiol Spectr. 2021 Sep 3;9(1):e0032121. doi: 10.1128/Spectrum.00321-21. Epub 2021 Jun 23. Microbiol Spectr. 2021. PMID: 34160280 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Characterization of Calcineurin-Responsive Transcription Factors Fg01341 and Fg01350 in Fusarium graminearum.Front Microbiol. 2020 Nov 26;11:597998. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.597998. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33324378 Free PMC article.
-
The role of Candida albicans stress response pathways in antifungal tolerance and resistance.iScience. 2022 Feb 19;25(3):103953. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.103953. eCollection 2022 Mar 18. iScience. 2022. PMID: 35281744 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Transient Receptor Potential Channel Yvc1 Deletion Recovers the Growth Defect of Calcineurin Mutant Under Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Candida albicans.Front Microbiol. 2021 Nov 30;12:752670. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.752670. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34917046 Free PMC article.
-
A functionally divergent intrinsically disordered region underlying the conservation of stochastic signaling.PLoS Genet. 2021 Sep 10;17(9):e1009629. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1009629. eCollection 2021 Sep. PLoS Genet. 2021. PMID: 34506483 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stewart AA, Ingebritsen TS, Manalan A, Klee CB, Cohen P. Discovery of a Ca2+-dependent and calmodulin-dependent protein phosphatase—probable identity with calcineurin (Cam-Bp80). FEBS Letters. 1982;137(1):80–4. - PubMed
-
- Liu J, Farmer JD, Lane WS, Friedman J, Weissman I, Schreiber SL. Calcineurin is a common target of cyclophilin-cyclosporine-A and FKBP-FK506 complexes. Cell. 1991;66(4):807–15. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

