Next-Generation CDK2/9 Inhibitors and Anaphase Catastrophe in Lung Cancer
- PMID: 28376145
- PMCID: PMC6059250
- DOI: 10.1093/jnci/djw297
Next-Generation CDK2/9 Inhibitors and Anaphase Catastrophe in Lung Cancer
Abstract
Background: The first generation CDK2/7/9 inhibitor seliciclib (CYC202) causes multipolar anaphase and apoptosis in lung cancer cells with supernumerary centrosomes (known as anaphase catastrophe). We investigated a new and potent CDK2/9 inhibitor, CCT68127 (Cyclacel).
Methods: CCT68127 was studied in lung cancer cells (three murine and five human) and control murine pulmonary epithelial and human immortalized bronchial epithelial cells. Robotic CCT68127 cell-based proliferation screens were used. Cells undergoing multipolar anaphase and inhibited centrosome clustering were scored. Reverse phase protein arrays (RPPAs) assessed CCT68127 effects on signaling pathways. The function of PEA15, a growth regulator highlighted by RPPAs, was analyzed. Syngeneic murine lung cancer xenografts (n = 4/group) determined CCT68127 effects on tumorigenicity and circulating tumor cell levels. All statistical tests were two-sided.
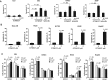
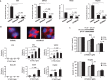
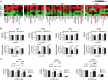
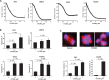
Results: CCT68127 inhibited growth up to 88.5% (SD = 6.4%, P < .003) at 1 μM, induced apoptosis up to 42.6% (SD = 5.5%, P < .001) at 2 μM, and caused G1 or G2/M arrest in lung cancer cells with minimal effects on control cells (growth inhibition at 1 μM: 10.6%, SD = 3.6%, P = .32; apoptosis at 2 μM: 8.2%, SD = 1.0%, P = .22). A robotic screen found that lung cancer cells with KRAS mutation were particularly sensitive to CCT68127 ( P = .02 for IC 50 ). CCT68127 inhibited supernumerary centrosome clustering and caused anaphase catastrophe by 14.1% (SD = 3.6%, P < .009 at 1 μM). CCT68127 reduced PEA15 phosphorylation by 70% (SD = 3.0%, P = .003). The gain of PEA15 expression antagonized and its loss enhanced CCT68127-mediated growth inhibition. CCT68127 reduced lung cancer growth in vivo ( P < .001) and circulating tumor cells ( P = .004). Findings were confirmed with another CDK2/9 inhibitor, CYC065.
Conclusions: Next-generation CDK2/9 inhibition elicits marked antineoplastic effects in lung cancer via anaphase catastrophe and reduced PEA15 phosphorylation.
© The Author 2017. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures




Similar articles
-
CDK2 Inhibition Causes Anaphase Catastrophe in Lung Cancer through the Centrosomal Protein CP110.Cancer Res. 2015 May 15;75(10):2029-38. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-1494. Epub 2015 Mar 25. Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 25808870 Free PMC article.
-
Specific CP110 Phosphorylation Sites Mediate Anaphase Catastrophe after CDK2 Inhibition: Evidence for Cooperation with USP33 Knockdown.Mol Cancer Ther. 2015 Nov;14(11):2576-85. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-15-0443. Epub 2015 Aug 24. Mol Cancer Ther. 2015. PMID: 26304236 Free PMC article.
-
Dinaciclib Induces Anaphase Catastrophe in Lung Cancer Cells via Inhibition of Cyclin-Dependent Kinases 1 and 2.Mol Cancer Ther. 2016 Nov;15(11):2758-2766. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-16-0127. Epub 2016 Aug 22. Mol Cancer Ther. 2016. PMID: 27550941 Free PMC article.
-
Engaging Anaphase Catastrophe Mechanisms to Eradicate Aneuploid Cancers.Mol Cancer Ther. 2018 Apr;17(4):724-731. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-17-1108. Epub 2018 Mar 20. Mol Cancer Ther. 2018. PMID: 29559545 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting CDK2 in cancer: challenges and opportunities for therapy.Drug Discov Today. 2020 Feb;25(2):406-413. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2019.12.001. Epub 2019 Dec 10. Drug Discov Today. 2020. PMID: 31839441 Review.
Cited by
-
A rapid and sensitive bioanalytical LC-MS/MS method for the quantitation of a novel CDK5 inhibitor 20-223 (CP668863) in plasma: Application to in vitro metabolism and plasma protein-binding studies.Biomed Chromatogr. 2020 Aug;34(8):e4859. doi: 10.1002/bmc.4859. Epub 2020 May 18. Biomed Chromatogr. 2020. PMID: 32307720 Free PMC article.
-
LINC00265 Promotes Metastasis and Progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Interacting with E2F1 at The Promoter of CDK2.Cell J. 2022 Jun;24(6):294-301. doi: 10.22074/cellj.2022.8035. Epub 2022 Jun 29. Cell J. 2022. PMID: 35892231 Free PMC article.
-
A Precision Medicine Drug Discovery Pipeline Identifies Combined CDK2 and 9 Inhibition as a Novel Therapeutic Strategy in Colorectal Cancer.Mol Cancer Ther. 2020 Dec;19(12):2516-2527. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-20-0454. Epub 2020 Nov 6. Mol Cancer Ther. 2020. PMID: 33158998 Free PMC article.
-
Cigarette smoke condensate induces centrosome clustering in normal lung epithelial cells.Cancer Med. 2023 Apr;12(7):8499-8509. doi: 10.1002/cam4.5599. Epub 2023 Jan 9. Cancer Med. 2023. PMID: 36621828 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclin-dependent protein kinases and cell cycle regulation in biology and disease.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2025 Jan 13;10(1):11. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-02080-z. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2025. PMID: 39800748 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, et al.Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;652:87–108. - PubMed
-
- Torre LA, Siegel RL, Ward EM, et al.Global cancer incidence and mortality rates and trends-an update. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2016;251:16–27. - PubMed
-
- Shapiro GI. Cyclin-dependent kinase pathways as targets for cancer treatment. J Clin Oncol. 2006;2411:1770–1783. - PubMed
-
- Freemantle SJ, Liu X, Feng Q, et al.Cyclin degradation for cancer therapy and chemoprevention. J Cell Biochem. 2007;1024:869–877. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

