Sequential Validation of Blood-Based Protein Biomarker Candidates for Early-Stage Pancreatic Cancer
- PMID: 28376157
- PMCID: PMC5441297
- DOI: 10.1093/jnci/djw266
Sequential Validation of Blood-Based Protein Biomarker Candidates for Early-Stage Pancreatic Cancer
Abstract
Background: CA19-9, which is currently in clinical use as a pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) biomarker, has limited performance in detecting early-stage disease. We and others have identified protein biomarker candidates that have the potential to complement CA19-9. We have carried out sequential validations starting with 17 protein biomarker candidates to determine which markers and marker combination would improve detection of early-stage disease compared with CA19-9 alone.
Methods: Candidate biomarkers were subjected to enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay based sequential validation using independent multiple sample cohorts consisting of PDAC cases (n = 187), benign pancreatic disease (n = 93), and healthy controls (n = 169). A biomarker panel for early-stage PDAC was developed based on a logistic regression model. All statistical tests for the results presented below were one-sided.
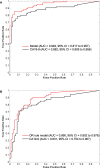
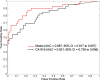
Results: Six out of the 17 biomarker candidates and CA19-9 were validated in a sample set consisting of 75 PDAC patients, 27 healthy subjects, and 19 chronic pancreatitis patients. A second independent set of 73 early-stage PDAC patients, 60 healthy subjects, and 74 benign pancreatic disease patients (combined validation set) yielded a model that consisted of TIMP1, LRG1, and CA19-9. Additional blinded testing of the model was done using an independent set of plasma samples from 39 resectable PDAC patients and 82 matched healthy subjects (test set). The model yielded areas under the curve (AUCs) of 0.949 (95% confidence interval [CI] = 0.917 to 0.981) and 0.887 (95% CI = 0.817 to 0.957) with sensitivities of 0.849 and 0.667 at 95% specificity in discriminating early-stage PDAC vs healthy subjects in the combined validation and test sets, respectively. The performance of the biomarker panel was statistically significantly improved compared with CA19-9 alone (P < .001, combined validation set; P = .008, test set).
Conclusion: The addition of TIMP1 and LRG1 immunoassays to CA19-9 statistically significantly improves the detection of early-stage PDAC.
© The Author 2016. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

