Keystone predation and molecules of keystone significance
- PMID: 28376248
- PMCID: PMC5598783
- DOI: 10.1002/ecy.1849
Keystone predation and molecules of keystone significance
Abstract
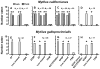
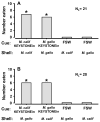
Keystone species structure ecological communities and are major determinants of biodiversity. A synthesis of research on keystone species is nonetheless missing a critical component - the sensory mechanisms for behavioral interactions that determine population- and community-wide attributes. Here, we establish the chemosensory basis for keystone predation by sea stars (Pisaster ochraceus) on mussels. This consumer-resource interaction is prototypic of top-down driven trophic cascades. Each mussel species (Mytilus californianus and M. galloprovincialis) secretes a glycoprotein orthologue (29.6 and 28.1 kDa, respectively) that acts, singularly, to evoke the sea star predatory response. The orthologues (named "KEYSTONEin") are localized in the epidermis, extrapallial fluid, and organic shell coating (periostracum) of live, intact mussels. Thus, KEYSTONEin contacts chemosensory receptors on tube feet as sea stars crawl over rocky surfaces in search of prey. The complete nucleotide sequences reveal that KEYSTONEin shares 87% (M. californianus) or 98% (M. galloprovincialis) homology with a calcium-binding protein in the shell matrix of a closely related congener, M. edulis. All three molecules cluster tightly within the Complement Component 1 Domain Containing (C1qDC) protein family; each exhibits a large globular domain, low complexity region(s), coiled coil, and at least four of five histidine-aspartic acid tandem motifs. Collective results support the hypothesis that KEYSTONEin evolved ancestrally in immunological, and later, in biomineralization roles. More recently, the substance has become exploited by sea stars as a contact cue for prey recognition. As the first identified compound to evoke keystone predation, KEYSTONEin provides valuable sensory information, promotes biodiversity, and shapes community structure and function. Without this molecule, there would be no predation by sea stars on mussels.
Keywords: Mytilus californianus; Mytilus galloprovincialis; Pisaster ochraceus; chemical cue; community ecology; foundation species; glycoprotein; intertidal ecology; keystone predation; mussel; sea star; sensory ecology.
© 2017 by the Ecological Society of America.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Finding food: how generalist predators use contact-chemosensory information to guide prey preferences.J Exp Biol. 2024 Oct 1;227(19):jeb247523. doi: 10.1242/jeb.247523. Epub 2024 Oct 7. J Exp Biol. 2024. PMID: 39246153 Free PMC article.
-
Revisiting Paine's 1966 Sea Star Removal Experiment, the Most-Cited Empirical Article in the American Naturalist.Am Nat. 2016 Oct;188(4):365-78. doi: 10.1086/688045. Epub 2016 Aug 8. Am Nat. 2016. PMID: 27622872
-
Expansion of intertidal mussel beds following disease-driven reduction of a keystone predator.Mar Environ Res. 2021 Jul;169:105363. doi: 10.1016/j.marenvres.2021.105363. Epub 2021 May 14. Mar Environ Res. 2021. PMID: 34030089
-
Neuroecology, chemical defense, and the keystone species concept.Biol Bull. 2007 Dec;213(3):208-25. doi: 10.2307/25066641. Biol Bull. 2007. PMID: 18083963 Review.
-
The environmentally tuned transcriptomes of Mytilus mussels.J Exp Biol. 2015 Jun;218(Pt 12):1822-33. doi: 10.1242/jeb.118190. J Exp Biol. 2015. PMID: 26085660 Review.
Cited by
-
Finding food: how generalist predators use contact-chemosensory information to guide prey preferences.J Exp Biol. 2024 Oct 1;227(19):jeb247523. doi: 10.1242/jeb.247523. Epub 2024 Oct 7. J Exp Biol. 2024. PMID: 39246153 Free PMC article.
-
Invertebrate C1q Domain-Containing Proteins: Molecular Structure, Functional Properties and Biomedical Potential.Mar Drugs. 2023 Oct 30;21(11):570. doi: 10.3390/md21110570. Mar Drugs. 2023. PMID: 37999394 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Low abundance members of the gut microbiome exhibit high immunogenicity.Gut Microbes. 2022 Jan-Dec;14(1):2104086. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2022.2104086. Gut Microbes. 2022. PMID: 35881003 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel C1q Domain-Containing Protein Isolated from the Mollusk Modiolus kurilensis Recognizing Glycans Enriched with Acidic Galactans and Mannans.Mar Drugs. 2021 Nov 26;19(12):668. doi: 10.3390/md19120668. Mar Drugs. 2021. PMID: 34940667 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blanchette CA, Helmuth B, Gaines SD. Spatial patterns of growth in the mussel, Mytilus californianus, across a major oceanographic and biogeographic boundary at Point Conception, California, USA. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology. 2007;340:126–148.
-
- Boxshall AJ. The importance of flow and settlement cues to larvae of the abalone, Haliotis rufescens. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology. 2000;254:143–167. - PubMed
-
- Bradford MM. A rapid and sensitive method for quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Analytical Biochemistry. 1976;72:248–254. - PubMed
-
- Carland TM, Gerwick L. The C1q domain containing proteins: where do they come from and what do they do? Developmental and Comparative Immunology. 2010;34:785–790. - PubMed
-
- Caskey L, Hasenstein KH, Bauer RT. Studies on contact sex pheromones of the caridean shrimp Palaemonetes pugio: I. Cuticular hydrocarbons associated with mate recognition. Invertebrate Reproduction and Development. 2009a;53:930–103.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
