Mycophenolate Mofetil Versus Placebo for Systemic Sclerosis-Related Interstitial Lung Disease: An Analysis of Scleroderma Lung Studies I and II
- PMID: 28376288
- PMCID: PMC5560126
- DOI: 10.1002/art.40114
Mycophenolate Mofetil Versus Placebo for Systemic Sclerosis-Related Interstitial Lung Disease: An Analysis of Scleroderma Lung Studies I and II
Abstract
Objective: To compare mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) with placebo for the treatment of systemic sclerosis (SSc)-related interstitial lung disease (ILD).
Methods: We included participants enrolled in the placebo arm of Scleroderma Lung Study (SLS) I and the MMF arm of SLS II. SLS I randomized participants to receive either oral cyclophosphamide (CYC) or placebo for 1 year, while SLS II randomized participants to receive either MMF for 2 years or oral CYC for 1 year followed by 1 year of placebo. Eligibility criteria for SLS I and SLS II were nearly identical. The primary outcome was % predicted forced vital capacity (FVC), and key secondary outcomes included % predicted diffusing capacity for carbon monoxide (DLco), the modified Rodnan skin thickness score (MRSS), and dyspnea. Joint models were created to evaluate the treatment effect on the course of these outcomes over 2 years.
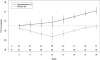
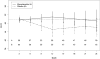
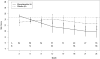
Results: At baseline, the MMF-treated group in SLS II (n = 69) and the placebo-treated group in SLS I (n = 79) had similar percentages of men and women and similar disease duration, SSc subtype, extent of skin disease, and % predicted FVC. MMF-treated patients in SLS II were slightly older (mean ± SD age 52.6 ± 9.7 years versus 48.1 ± 12.4 years; P = 0.0152) and had higher % predicted DLco (mean ± SD 54.0 ± 11.1 versus 46.2 ± 13.3; P = 0.0002) than placebo-treated patients in SLS I. After adjustment for baseline disease severity, treatment with MMF in comparison with placebo was associated with improved % predicted FVC (P < 0.0001), % predicted DLco (P < 0.0001), MRSS (P < 0.0001), and dyspnea (P = 0.0112) over 2 years.
Conclusion: Although there are inherent limitations in comparing participants from different trials, treatment with MMF was associated with improvements in physiologic outcomes and dyspnea compared with placebo, even after accounting for baseline disease severity. These results further substantiate the use of MMF for the treatment of SSc-related ILD.
© 2017, American College of Rheumatology.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Elhai M, Meune C, Avouac J, Kahan A, Allanore Trends in mortality in patients with systemic sclerosis over 40 years: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. Rheumatol (Oxford) 2012;51:1017–26. - PubMed
-
- Tyndall AJ, Bannert B, Vonk M, Airo P, Cozzi F, Carreira PE, et al. Causes and risk factors for death in systemic sclerosis: a study from the EULAR Scleroderma Trials and Research (EUSTAR) database. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010;69:1809–15. - PubMed
-
- Tashkin DP, Elashoff R, Clements PJ, Goldin J, Roth M, Furst DE, et al. Cyclophosphamide versus placebo in scleroderma lung disease. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:2655–66. - PubMed
-
- Hoyles RK, Ellis RW, Wellsbury J, Lees B, Newlands P, Goh NS, et al. A multicenter, prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of corticosteroids and intravenous cyclophosphamide followed by oral azathioprine for the treatment of pulmonary fibrosis in scleroderma. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54:3962–70. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

