Origins of PDZ Binding Specificity. A Computational and Experimental Study Using NHERF1 and the Parathyroid Hormone Receptor
- PMID: 28376304
- PMCID: PMC5479578
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.biochem.7b00078
Origins of PDZ Binding Specificity. A Computational and Experimental Study Using NHERF1 and the Parathyroid Hormone Receptor
Abstract
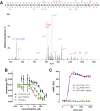
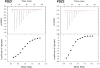
Na+/H+ exchanger regulatory factor-1 (NHERF1) is a scaffolding protein containing two PSD95/discs large protein/ZO1 (PDZ) domains that modifies the signaling, trafficking, and function of the parathyroid hormone receptor (PTHR), a family B G-protein-coupled receptor. PTHR and NHERF1 bind through a PDZ-ligand-recognition mechanism. We show that PTH elicits phosphorylation of Thr591 in the canonical -ETVM binding motif of PTHR. Conservative substitution of Thr591 with Cys does not affect PTH(1-34)-induced cAMP production or binding of PTHR to NHERF1. The findings suggested the presence of additional sites upstream of the PDZ-ligand motif through which the two proteins interact. Structural determinants outside the canonical NHERF1 PDZ-PTHR interface that influence binding have not been characterized. We used molecular dynamics (MD) simulation to predict residues involved in these interactions. Simulation data demonstrate that the negatively charged Glu side chains at positions -3, -5, and -6 upstream of the PDZ binding motif are involved in PDZ-PTHR recognition. Engineered mutant peptides representing the PTHR C-terminal region were used to measure the binding affinity with NHERF1 PDZ domains. Comparable micromolar affinities for peptides of different length were confirmed by fluorescence polarization, isothermal titration calorimetry, and surface plasmon resonance. Binding affinities measured for Ala variants validate MD simulations. The linear relation between the change in enthalpy and entropy following Ala substitutions at upstream positions -3, -5, and -6 of the PTHR peptide provides a clear example of the thermodynamic compensation rule. Overall, our data highlight sequences in PTHR that contribute to NHERF1 interaction and can be altered to prevent phosphorylation-mediated inhibition.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Noncanonical Sequences Involving NHERF1 Interaction with NPT2A Govern Hormone-Regulated Phosphate Transport: Binding Outside the Box.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 22;22(3):1087. doi: 10.3390/ijms22031087. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33499384 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural basis for NHERF1 PDZ domain binding.Biochemistry. 2012 Apr 10;51(14):3110-20. doi: 10.1021/bi201213w. Epub 2012 Mar 27. Biochemistry. 2012. PMID: 22429102 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic Na+-H+ exchanger regulatory factor-1 association and dissociation regulate parathyroid hormone receptor trafficking at membrane microdomains.J Biol Chem. 2011 Oct 7;286(40):35020-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.264978. Epub 2011 Aug 8. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21832055 Free PMC article.
-
Multisite NHERF1 phosphorylation controls GRK6A regulation of hormone-sensitive phosphate transport.J Biol Chem. 2021 Jan-Jun;296:100473. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100473. Epub 2021 Feb 24. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33639163 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the PDZ-scaffold protein NHERF1/EBP50 in cancer biology: from signaling regulation to clinical relevance.Oncogene. 2017 Jun 1;36(22):3067-3079. doi: 10.1038/onc.2016.462. Epub 2017 Jan 9. Oncogene. 2017. PMID: 28068322 Review.
Cited by
-
Mutations in an unrecognized internal NPT2A PDZ motif disrupt phosphate transport and cause congenital hypophosphatemia.Biochem J. 2023 May 17;480(9):685-699. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20230020. Biochem J. 2023. PMID: 37132631 Free PMC article.
-
Noncanonical Sequences Involving NHERF1 Interaction with NPT2A Govern Hormone-Regulated Phosphate Transport: Binding Outside the Box.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 22;22(3):1087. doi: 10.3390/ijms22031087. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33499384 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynamic structure of the full-length scaffolding protein NHERF1 influences signaling complex assembly.J Biol Chem. 2019 Jul 19;294(29):11297-11310. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.008218. Epub 2019 Jun 6. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 31171716 Free PMC article.
-
The molecular sociology of NHERF1 PDZ proteins controlling renal hormone-regulated phosphate transport.Biosci Rep. 2024 Mar 27;44(3):BSR20231380. doi: 10.1042/BSR20231380. Biosci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38465463 Free PMC article.
-
The Intricacies of Renal Phosphate Reabsorption-An Overview.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 25;25(9):4684. doi: 10.3390/ijms25094684. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38731904 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wang B, Bisello A, Yang Y, Romero GG, Friedman PA. NHERF1 regulates parathyroid hormone receptor membrane retention without affecting recycling. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:36214–36222. - PubMed
-
- Mahon MJ, Donowitz M, Yun CC, Segre GV. Na+/H+ exchanger regulatory factor 2 directs parathyroid hormone 1 receptor signalling. Nature. 2002;417:858–861. - PubMed
-
- Voltz JW, Weinman EJ, Shenolikar S. Expanding the role of NHERF, a PDZ-domain containing protein adapter, to growth regulation. Oncogene. 2001;20:6309–6314. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

