Subclinical Peroneal Neuropathy: A Common, Unrecognized, and Preventable Finding Associated With a Recent History of Falling in Hospitalized Patients
- PMID: 28376439
- PMCID: PMC5389395
- DOI: 10.1370/afm.1973
Subclinical Peroneal Neuropathy: A Common, Unrecognized, and Preventable Finding Associated With a Recent History of Falling in Hospitalized Patients
Abstract
Purpose: Identification of modifiable risk factors for falling is paramount in reducing the incidence and morbidity of falling. Peroneal neuropathy with an overt foot drop is a known risk factor for falling, but research into subclinical peroneal neuropathy (SCPN) resulting from compression at the fibular head is lacking. The purpose of our study was to determine the prevalence of SCPN in hospitalized patients and establish whether it is associated with a recent history of falling.
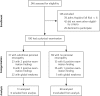
Methods: We conducted a cross-sectional study of 100 medical inpatients at a large academic tertiary care hospital in St Louis, Missouri. General medical inpatients deemed at moderate to high risk for falling were enrolled in the summer of 2013. Patients were examined for findings that suggest peroneal neuropathy, fall risk, and a history of falling. Multivariate logistic regression was used to correlate SCPN with fall risk and a history of falls in the past year.
Results: The mean patient age was 53 years (SD = 13 years), and 59 patients (59%) were female. Thirty-one patients had examination findings consistent with SCPN. After accounting for various confounding variables within a multivariate logistic regression model, patients with SCPN were 4.7 times (95% CI, 1.4-15.9) more likely to report having fallen 1 or more times in the past year.
Conclusions: Subclinical peroneal neuropathy is common in medical inpatients and is associated with a recent history of falling. Preventing or identifying SCPN in hospitalized patients provides an opportunity to modify activity and therapy, potentially reducing risk.
Keywords: accidental; common peroneal; falls; nerve compression syndromes; neuropathy; peroneal nerve diseases; peroneal nerve paralysis; preventive medicine.
© 2016 Annals of Family Medicine, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Brandis S. A collaborative occupational therapy and nursing approach to falls prevention in hospital inpatients. J Qual Clin Pract. 1999; 19(4): 215–220. - PubMed
-
- Oliver D, Healey F, Haines TP. Preventing falls and fall-related injuries in hospitals. Clin Geriatr Med. 2010; 26(4): 645–692. - PubMed
-
- Ellis AA, Trent RB. Do the risks and consequences of hospitalized fall injuries among older adults in California vary by type of fall? J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2001; 56(11): M686–M692. - PubMed
-
- Bouche P. Compression and entrapment neuropathies. In: Gérard S, Christian K, eds. Handbook of Clinical Neurology. Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier; 2013: 311–66. - PubMed
-
- Craig A. Entrapment neuropathies of the lower extremity. PM R. 2013; 5(5)(Suppl): S31–S40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous