KALK study: ultrasound guided needling and lavage (barbotage) with steroid injection versus sham barbotage with and without steroid injection - protocol for a randomized, double-blinded, controlled, multicenter study
- PMID: 28376756
- PMCID: PMC5379547
- DOI: 10.1186/s12891-017-1501-9
KALK study: ultrasound guided needling and lavage (barbotage) with steroid injection versus sham barbotage with and without steroid injection - protocol for a randomized, double-blinded, controlled, multicenter study
Abstract
Background: For the treatment of calcific tendinitis of the shoulder a variety of treatment regimes exist. Commonly used treatment measures include medication with oral analgesics, corticosteroid injections, extracorporeal shockwave therapy, ultrasound guided needling and lavage, and surgical treatment. Earlier cohort studies suggest that patients may benefit from these treatments, but there are few randomized studies and conflicting evidence about the effectiveness of the various treatments. In the present study we aim to compare the effectiveness of ultrasound guided needling and lavage (barbotage) together with a steroid injection to sham barbotage with and without an additional steroid injection.
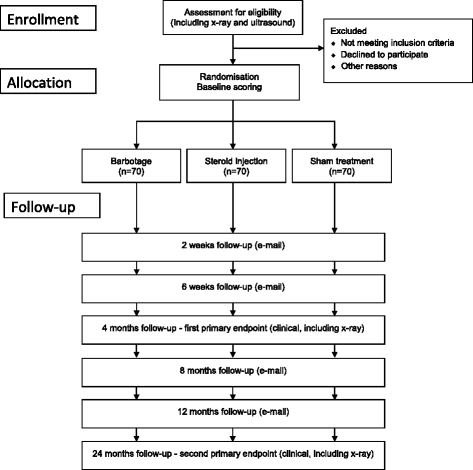
Methods: The study will be performed in six secondary-care institutions in Norway and Sweden. It is designed as a pragmatic, randomized, three-arm, parallel group, double-blinded, sham-controlled clinical trial with a 2-year follow-up. It will be performed on 210 patients, aged 30 years or older, presenting with painful arc, positive impingement sign and a calcium deposit > 5 mm. Randomization to one of the three treatment options will be performed by using an online central randomization system. The three treatment groups are barbotage together with a subacromial steroid injection (the barbotage group), sham barbotage together with a subacromial steroid injection (the steroid group) or sham barbotage without a subacromial steroid injection (the placebo group). In the placebo group the steroid injection will be replaced by a short-acting local anaesthetic. Standardized home-based post-treatment physiotherapy will be performed by all patients for 8 weeks. Follow-ups are at 2 and 6 weeks, 4, 8, 12 and 24 months after treatment was given and will be performed with the patients and the outcome assessors blinded for group assignment. Primary outcome will be the Oxford shoulder score at 4 month follow-up. Secondary outcome measures are the QuickDASH upper extremity score, the EQ-5D-5L general health score and visual analogue scales for pain at rest, during activity, and at night.
Discussion: The scientific evidence from this placebo-controlled trial will be of importance for future treatment recommendations in patients with calcific tendinitis.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT02419040 , registered 10 April 2015 EudraCT: 2015-002343-34, registered 23 September 2015 (retrospectively registered).
Keywords: Barbotage; Calcific tendinitis; Corticosteroids; Placebo; Sham treatment; Ultrasound guided lavage.
References
-
- Bosworth BM. Calcium deposits in the shoulder and subacromial bursitis. A survey of 12122 shoulders. JAMA. 1941;116(22):2477–82. doi: 10.1001/jama.1941.02820220019004. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous