SMARCE1 is required for the invasive progression of in situ cancers
- PMID: 28377514
- PMCID: PMC5402464
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1703931114
SMARCE1 is required for the invasive progression of in situ cancers
Abstract
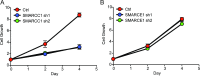
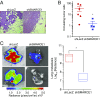
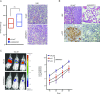
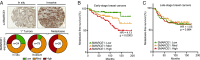
Advances in mammography have sparked an exponential increase in the detection of early-stage breast lesions, most commonly ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS). More than 50% of DCIS lesions are benign and will remain indolent, never progressing to invasive cancers. However, the factors that promote DCIS invasion remain poorly understood. Here, we show that SMARCE1 is required for the invasive progression of DCIS and other early-stage tumors. We show that SMARCE1 drives invasion by regulating the expression of secreted proteases that degrade basement membrane, an ECM barrier surrounding all epithelial tissues. In functional studies, SMARCE1 promotes invasion of in situ cancers growing within primary human mammary tissues and is also required for metastasis in vivo. Mechanistically, SMARCE1 drives invasion by forming a SWI/SNF-independent complex with the transcription factor ILF3. In patients diagnosed with early-stage cancers, SMARCE1 expression is a strong predictor of eventual relapse and metastasis. Collectively, these findings establish SMARCE1 as a key driver of invasive progression in early-stage tumors.
Keywords: DCIS; SMARCE1; biomarker; invasive progression.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
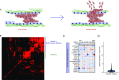
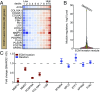

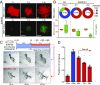
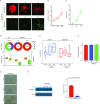


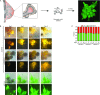
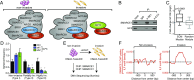
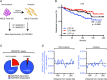
References
-
- Howlader N, et al. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975-2013. National Cancer Institute; Bethesda, MD: 2016.
-
- Schuetz CS, et al. Progression-specific genes identified by expression profiling of matched ductal carcinomas in situ and invasive breast tumors, combining laser capture microdissection and oligonucleotide microarray analysis. Cancer Res. 2006;66:5278–5286. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

