Topoisomerase II Inhibitors Induce DNA Damage-Dependent Interferon Responses Circumventing Ebola Virus Immune Evasion
- PMID: 28377530
- PMCID: PMC5380843
- DOI: 10.1128/mBio.00368-17
Topoisomerase II Inhibitors Induce DNA Damage-Dependent Interferon Responses Circumventing Ebola Virus Immune Evasion
Abstract
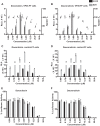
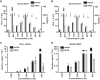
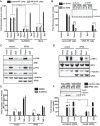
Ebola virus (EBOV) protein VP35 inhibits production of interferon alpha/beta (IFN) by blocking RIG-I-like receptor signaling pathways, thereby promoting virus replication and pathogenesis. A high-throughput screening assay, developed to identify compounds that either inhibit or bypass VP35 IFN-antagonist function, identified five DNA intercalators as reproducible hits from a library of bioactive compounds. Four, including doxorubicin and daunorubicin, are anthracycline antibiotics that inhibit topoisomerase II and are used clinically as chemotherapeutic drugs. These compounds were demonstrated to induce IFN responses in an ATM kinase-dependent manner and to also trigger the DNA-sensing cGAS-STING pathway of IFN induction. These compounds also suppress EBOV replication in vitro and induce IFN in the presence of IFN-antagonist proteins from multiple negative-sense RNA viruses. These findings provide new insights into signaling pathways activated by important chemotherapy drugs and identify a novel therapeutic approach for IFN induction that may be exploited to inhibit RNA virus replication.IMPORTANCE Ebola virus and other emerging RNA viruses are significant but unpredictable public health threats. Therapeutic approaches with broad-spectrum activity could provide an attractive response to such infections. We describe a novel assay that can identify small molecules that overcome Ebola virus-encoded innate immune evasion mechanisms. This assay identified as hits cancer chemotherapeutic drugs, including doxorubicin. Follow-up studies provide new insight into how doxorubicin induces interferon (IFN) responses, revealing activation of both the DNA damage response kinase ATM and the DNA sensor cGAS and its partner signaling protein STING. The studies further demonstrate that the ATM and cGAS-STING pathways of IFN induction are a point of vulnerability not only for Ebola virus but for other RNA viruses as well, because viral innate immune antagonists consistently fail to block these signals. These studies thereby define a novel avenue for therapeutic intervention against emerging RNA viruses.
Keywords: ATM signaling; DNA damage; Ebola virus; cGAS-STING pathway; innate immune responses.
Copyright © 2017 Luthra et al.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Inhibiting pyrimidine biosynthesis impairs Ebola virus replication through depletion of nucleoside pools and activation of innate immune responses.Antiviral Res. 2018 Oct;158:288-302. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2018.08.012. Epub 2018 Aug 23. Antiviral Res. 2018. PMID: 30144461 Free PMC article.
-
Cynarin blocks Ebola virus replication by counteracting VP35 inhibition of interferon-beta production.Antiviral Res. 2022 Feb;198:105251. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2022.105251. Epub 2022 Jan 20. Antiviral Res. 2022. PMID: 35066016
-
Evasion of interferon responses by Ebola and Marburg viruses.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2009 Sep;29(9):511-20. doi: 10.1089/jir.2009.0076. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2009. PMID: 19694547 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Innate Immune Responses of Bat and Human Cells to Filoviruses: Commonalities and Distinctions.J Virol. 2017 Mar 29;91(8):e02471-16. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02471-16. Print 2017 Apr 15. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28122983 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into Ebola Virus VP35 and VP24 Interferon Inhibitory Functions and their Initial Exploitation as Drug Targets.Infect Disord Drug Targets. 2019;19(4):362-374. doi: 10.2174/1871526519666181123145540. Infect Disord Drug Targets. 2019. PMID: 30468131 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of cGAS/STING signaling and corresponding immune escape strategies of viruses.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Sep 14;12:954581. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.954581. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36189363 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabologenomics approach to the discovery of novel compounds from Streptomyces sp. GMR22 as anti-SARS-CoV-2 drugs.Heliyon. 2021 Nov;7(11):e08308. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e08308. Epub 2021 Nov 2. Heliyon. 2021. PMID: 34746476 Free PMC article.
-
Long noncoding RNA CHROMR regulates antiviral immunity in humans.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Sep 13;119(37):e2210321119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2210321119. Epub 2022 Aug 24. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 36001732 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging Alphaviruses Are Sensitive to Cellular States Induced by a Novel Small-Molecule Agonist of the STING Pathway.J Virol. 2018 Feb 26;92(6):e01913-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01913-17. Print 2018 Mar 15. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29263267 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of PARP1 Dampens Pseudorabies Virus Infection through DNA Damage-Induced Antiviral Innate Immunity.J Virol. 2021 Jul 26;95(16):e0076021. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00760-21. Epub 2021 Jul 26. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 34037418 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

