Adverse reaction to metal debris with concomitant incidental crystalline arthropathy in hip arthroplasty
- PMID: 28378001
- PMCID: PMC5365402
- DOI: 10.1016/j.artd.2016.10.005
Adverse reaction to metal debris with concomitant incidental crystalline arthropathy in hip arthroplasty
Abstract
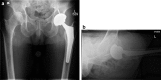
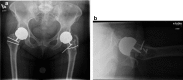
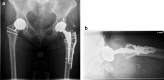
Adverse reaction to metal debris (ARMD) is a known cause of failed metal in hip arthroplasty. Diagnosis of this type of prosthesis failure may be difficult, and the hallmark is an abnormally elevated serum cobalt level. Concomitant diagnoses may also be present, such as infection, instability, and loosening, and this may confuse interpretation of abnormal laboratories. We present here, for the first time, 2 patients with ARMD and crystalline arthropathy. In each case, the patient chose surgery for ARMD, with resolution of symptoms and no recurrence of the crystalline arthropathy. We present these cases to alert the orthopaedist that crystalline arthropathy may be present at the same time as ARMD, but is likely not the primary cause of symptoms.
Keywords: Adverse reaction to metal debris; Crystalline arthropathy; Gout; Mechanically assisted crevice corrosion; Pseudogout.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Adverse reaction to metal debris with accompanying gout and amyloid deposits in hip arthroplasty.Radiol Case Rep. 2023 Jan 5;18(3):1005-1009. doi: 10.1016/j.radcr.2022.11.079. eCollection 2023 Mar. Radiol Case Rep. 2023. PMID: 36684621 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated Intra-Articular Cobalt and Chromium Levels in Mechanically Assisted Crevice Corrosion in Metal-on-Polyethylene Total Hip Arthroplasty.J Arthroplasty. 2017 May;32(5):1654-1658. doi: 10.1016/j.arth.2016.11.056. Epub 2016 Dec 14. J Arthroplasty. 2017. PMID: 28041772
-
Adverse reaction to metal debris after ReCap-M2A-Magnum large-diameter-head metal-on-metal total hip arthroplasty.Acta Orthop. 2013 Dec;84(6):549-54. doi: 10.3109/17453674.2013.859419. Epub 2013 Oct 31. Acta Orthop. 2013. PMID: 24171688 Free PMC article.
-
Distinguishing Periprosthetic Crystalline Arthropathy from Infection in Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review.J Knee Surg. 2022 May;35(6):668-675. doi: 10.1055/s-0040-1716507. Epub 2020 Sep 17. J Knee Surg. 2022. PMID: 32942331
-
Metal-on-Metal Hip Arthroplasty: A Comprehensive Review of the Current Literature.Cureus. 2023 Nov 3;15(11):e48238. doi: 10.7759/cureus.48238. eCollection 2023 Nov. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37929272 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Adverse reaction to metal debris with accompanying gout and amyloid deposits in hip arthroplasty.Radiol Case Rep. 2023 Jan 5;18(3):1005-1009. doi: 10.1016/j.radcr.2022.11.079. eCollection 2023 Mar. Radiol Case Rep. 2023. PMID: 36684621 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasound-based decision making following metal-on-metal hip arthroplasty.J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2020 Jan-Feb;11(1):79-84. doi: 10.1016/j.jcot.2019.04.009. Epub 2019 Apr 16. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2020. PMID: 32001990 Free PMC article.
-
Trunnionosis in total hip arthroplasty with accompanying amyloidosis and calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease.Radiol Case Rep. 2023 Oct 31;19(1):186-189. doi: 10.1016/j.radcr.2023.10.002. eCollection 2024 Jan. Radiol Case Rep. 2023. PMID: 38028302 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Harris W., Sledge C. Total hip and knee replacement. N Engl J Med. 1990;323:801. - PubMed
-
- Bohm E.R., Dunbar M.J., Frood J.J., Johnson T.M., Morris K.A. Rehospitalizations, early revisions, infections, and hospital resource use in the first year after hip and knee arthroplasties. J Arthroplasty. 2012;27:232. - PubMed
-
- Della Valle C., Parvizi J., Bauer T.W. The diagnosis of periprosthetic joint infections of the hip and knee. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2010;18:760. - PubMed
-
- McGrory B.J., MacKenzie J., Babikian G. A high prevalence of corrosion at the head-neck taper with contemporary Zimmer non-cemented hip components. J Arthroplasty. 2015;30(7):1265. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

