From Lipid Homeostasis to Differentiation: Old and New Functions of the Zinc Cluster Proteins Ecm22, Upc2, Sut1 and Sut2
- PMID: 28379181
- PMCID: PMC5412356
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms18040772
From Lipid Homeostasis to Differentiation: Old and New Functions of the Zinc Cluster Proteins Ecm22, Upc2, Sut1 and Sut2
Abstract
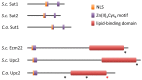
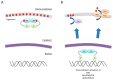
Zinc cluster proteins are a large family of transcriptional regulators with a wide range of biological functions. The zinc cluster proteins Ecm22, Upc2, Sut1 and Sut2 have initially been identified as regulators of sterol import in the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. These proteins also control adaptations to anaerobic growth, sterol biosynthesis as well as filamentation and mating. Orthologs of these zinc cluster proteins have been identified in several species of Candida. Upc2 plays a critical role in antifungal resistance in these important human fungal pathogens. Upc2 is therefore an interesting potential target for novel antifungals. In this review we discuss the functions, mode of actions and regulation of Ecm22, Upc2, Sut1 and Sut2 in budding yeast and Candida.
Keywords: Candida; anaerobic; antifungal; budding yeast; filamentation; mating; sterol biosynthesis; sterol uptake; transcription factor; zinc cluster protein.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

