Blood pressure lowering efficacy of renin inhibitors for primary hypertension
- PMID: 28379619
- PMCID: PMC6478238
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD007066.pub3
Blood pressure lowering efficacy of renin inhibitors for primary hypertension
Abstract
Background: Hypertension is a chronic condition associated with an increased risk of mortality and morbidity. Renin is the enzyme responsible for converting angiotensinogen to angiotensin I, which is then converted to angiotensin II. Renin inhibitors are a new class of drugs that decrease blood pressure (BP) by preventing the formation of both angiotensin I and angiotensin II.
Objectives: To quantify the dose-related BP lowering efficacy of renin inhibitors compared to placebo in the treatment of primary hypertension.To determine the change in BP variability, pulse pressure, and heart rate and to evaluate adverse events (mortality, non-fatal serious adverse events, total adverse events, withdrawal due to adverse effects and specific adverse events such as dry cough, diarrhoea and angioedema).
Search methods: The Cochrane Hypertension Information Specialist searched the following databases for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) up to February 2017: the Cochrane Hypertension Specialized Register, the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) (2017, Issue 2), MEDLINE (from 1946), Embase (from 1974), the World Health Organization International Clinical Trials Registry Platform, and ClinicalTrials.gov. There was no restriction by language or publication status. We also searched the European Medicines Agency (EMA) for clinical study reports, the Novartis Clinical Study Results Database, bibliographic citations from retrieved references, and contacted authors of relevant papers regarding further published and unpublished work.
Selection criteria: We included randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled studies evaluating BP lowering efficacy of fixed-dose monotherapy with renin inhibitor compared with placebo for a minimum duration of three to 12 weeks in adult patients with primary hypertension.
Data collection and analysis: This systematic review is a comprehensive update which includes four additional studies and extensive detail from nine clinical study reports (CSRs) of previously included studies obtained from EMA. The remaining three CSRs are not available.Two review authors independently assessed study eligibility and extracted data. In all cases where there was a difference between the CSR and the published report, data from the CSR was used. Dichotomous outcomes were reported as risk ratio (RR) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) and continuous outcomes as mean difference (MD) with 95% CIs.
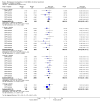
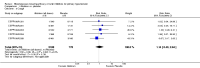
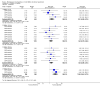
Main results: 12 studies (mean duration of eight weeks) in 7439 mostly Caucasian patients (mean age 54 years) with mild-to-moderate uncomplicated hypertension were eligible for inclusion in the review. Aliskiren was the only renin inhibitor evaluated. All included studies were assessed to have high likelihood of attrition, reporting and funding bias.Aliskiren has a dose-related systolic/diastolic blood pressure (SBP/DBP) lowering effect as compared with placebo MD with 95% CI: aliskiren 75 mg (MD -2.97, 95% CI -4.76 to -1.18)/(MD -2.05, 95% CI -3.13 to -0.96) mm Hg (moderate-quality evidence), aliskiren 150 mg (MD -5.95, 95% CI -6.85 to -5.06)/ (MD -3.16, 95% CI -3.74 to -2.58) mm Hg (moderate-quality evidence), aliskiren 300 mg (MD -7.88, 95% CI -8.94 to -6.82)/ (MD -4.49, 95% CI -5.17 to -3.82) mm Hg (moderate-quality evidence), aliskiren 600 mg (MD -11.35, 95% CI -14.43 to -8.27)/ (MD -5.86, 95% CI -7.73 to -3.99) mm Hg (low-quality evidence). There was a dose-dependent decrease in blood pressure for aliskiren 75 mg, 150 mg and 300 mg. The blood pressure lowering effect of aliskiren 600 mg was not different from 300 mg (MD -0.61, 95% CI -2.78 to 1.56)/(MD -0.68, 95% CI -2.03 to 0.67). Aliskiren had no effect on blood pressure variability. Due to very limited information available regarding change in heart rate and pulse pressure, it was not possible to meta-analyze these outcomes.Mortality and non-fatal serious adverse events were not increased. This review found that in studies of eight week duration aliskiren may not increase withdrawal due to adverse events (low-quality evidence). Diarrhoea was increased in a dose-dependent manner (RR 7.00, 95% CI 2.48 to 19.72) with aliskiren 600 mg (low-quality evidence). The most frequent adverse events reported were headache, nasopharyngitis, diarrhoea, dizziness and fatigue.
Authors' conclusions: Compared to placebo, aliskiren lowered BP and this effect is dose-dependent. This magnitude of BP lowering effect is similar to that for angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs). There is no difference in mortality, nonfatal serious adverse events or withdrawal due to adverse effects with short term aliskiren monotherapy. Diarrhoea was considerably increased with aliskiren 600 mg.
Conflict of interest statement
None known.
Figures


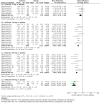
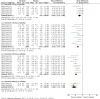
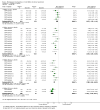
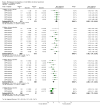










Update of
-
Blood pressure lowering efficacy of renin inhibitors for primary hypertension.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008 Oct 8;(4):CD007066. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007066.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Apr 05;4:CD007066. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007066.pub3. PMID: 18843743 Updated.
Comment in
-
The Efficacy of Renin Inhibitors in Primary Hypertension.Am J Nurs. 2018 Apr;118(4):56. doi: 10.1097/01.NAJ.0000532077.64748.d2. Am J Nurs. 2018. PMID: 29596257
References
References to studies included in this review
CSPA100A1301 {unpublished data only}
-
- Novartis. Efficacy and safety of SPA100 (fixed‐dose combination of aliskiren/amlodipine) in patients with essential hypertension. ClinicalTrials.gov identifier NCT01237223 May 11 2012:1‐27.
CSPA100A2305 {published data only}
-
- Littlejohn TW 3rd, Jones SW, Zhang J, Hsu H, Keefe DL. Efficacy and safety of aliskiren and amlodipine combination therapy in patients with hypertension: a randomized, double‐blind, multifactorial study. Journal of Human Hypertension 2013;27(5):321‐7. - PubMed
-
- Novartis. An 8‐week double‐blind, multicenter, randomized, multifactorial, placebo‐controlled, parallel group study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of aliskiren administered alone and in combination with amlodipine in patients with essential hypertension. Novartis Clinical Trial Results Database. 26th May 2010:1‐16. [Little John]
CSPP100A1201 {published data only}
-
- Kushiro T, Hiroshige I, Yoshihisa A, Hiromi G, Shinji T, Keefe D. Aliskiren, a novel oral renin inhibitor, provides dose‐dependent efficacy and placebo‐like tolerability in Japanese patients with hypertension. Hypertension Research ‐ Clinical & Experimental 2006;29(12):997‐1005. - PubMed
-
- Novartis. Dose‐finding study of SPP100 in essential hypertension. Clinical Study Report. European Medicines Agency October 13th 2005:10531‐665.
CSPP100A1301 {unpublished data only}
-
- Novartis. A randomized, double‐blind, placebo and active‐controlled, multicenter, parallel‐group study comparing SPP100 (Aliskiren) 150 mg to placebo and to Losartan 50 mg to evaluate efficacy, safety and pharmacokinetics in patients with mild to moderate essential hypertension. Clinical Study Report. European Medicines Agency January 10, 2008:1‐137.
CSPP100A2201 {published data only}
-
- Gradman A, Schmieder R, Lins R, Nussberger J, Chiang Y, Bedigian M. Aliskiren, a novel orally effective renin inhibitor, provides dose‐dependent antihypertensive efficacy and placebo‐like tolerability in hypertensive patients. Circulation 2005;111:1012‐8. - PubMed
-
- Novartis. A multicentre, randomized, double blind, placebo‐controlled, parallel‐group study comparing aliskiren 150 mg, 300 mg, and 600 mg and Irbesartan 150 mg in patients with mild‐to‐moderate essential hypertension. Clinical Study Report. European Medicines Agency April 1st 2004:1‐61.
-
- Nussberger J, Gradman AH, Schmieder RE, Lins RL, Chiang Y, Prescott MF. Plasma renin and the antihypertensive effect of the orally active renin inhibitor aliskiren in clinical hypertension. International Journal of Clinical Practice 2007;61(9):1461‐1468. - PubMed
CSPP100A2203 {published data only}
-
- Novartis. A randomized, double blind, multicentre, multifactorial, placebo‐controlled, parallel‐group study to confirm the efficacy and safety of aliskiren monotherapy, and evaluate efficacy and safety of combinations of aliskiren and valsartan in hypertensive patients. Clinical Study Report. European Medicines Agency June 8th 2005:1547‐1634.
-
- Pool J, Roland E, Schmieder M, Aldigier JC, Januszewicz A, Zidek W, Chiang Y, Satlin A. Aliskiren, an orally effective renin inhibitor, provides antihypertensive efficacy alone and in combination with valsartan. American Journal of Hypertension 2007;20(1):11‐20. - PubMed
CSPP100A2204 {published data only}
-
- Novartis. An 8 week, double‐blind, multicenter, randomized, multifactorial, placebo‐controlled, parallel group,study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of aliskiren administered alone and in combination with hydrochlorothiazide in patients with essential hypertension. Clinical Study Report. European Medicines Agency October 25th 2005:3354‐3454.
-
- Villamil A, Chrysant S, Calhoun D, Schober B, Hsu H, Matrisciano‐Dimichino L, Zhang J. Renin inhibition with aliskiren provides additive antihypertensive efficacy when used in combination with hydrochlorothiazide. Journal of hypertension 2007;25(1):217‐226. - PubMed
CSPP100A2308 {published data only}
-
- Novartis. An 8 week, randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, parallel group, multicenter, study comparing aliskiren 150 mg, 300 mg, and 600 mg to placebo in patients with essential hypertension. Clinical Study Report. European Medicines Agency November 1st 2005:8458‐543.
-
- Oh B, Mitchell J, Herron J, Chung J, Khan Ml, Keefe D. Aliskiren, an oral renin inhibitor, provides dose‐dependent efficacy and sustained 24‐hour blood pressure control in patients with hypertension. Journal of the Amarican College of Cardiology 2007;49(11):1157‐63. - PubMed
CSPP100A2323 {published data only}
-
- Novartis. A twenty six‐week, randomized, double‐blind, parallel group, multicenter, active‐controlled, dose titration study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of aliskiren compared to HCTZ with the optional addition of amlodipine, followed by a second twenty six weeks of blinded treatment, in patients with essential hypertension. Clinical Study Report. European Medicines Agency May 16th 2006:28012‐9161.
-
- Schmieder RE, Philipp T, Guerediaga J, Gorostidi M, Smith B, Weissbach N, et. al. Long‐term antihypertensive efficacy and safety of the Oral direct renin Inhibitor aliskiren. Circulation 2009;119:417‐25. - PubMed
CSPP100A2327 {published data only}
-
- Novartis. An eight‐week randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, parallel‐group, multicenter study comparing aliskiren 150 mg, 300 mg, and 600 mg to placebo in patients with essential hypertension. Clinical Study Report. European Medicines Agency September 2006:17604‐20246.
-
- Oparil S, Yarrows S, Patel SF, Ang H, Zhang J, Satlin A. Efficacy and safety of combined use of aliskiren and valsartan in patients with hypertension: a randomised, double‐blind trial. Lancet 2007;370(9583):221‐9. - PubMed
CSPP100A2328 {published data only}
-
- Novartis. A randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, parallel‐group, multicenter study comparing an eight‐week treatment of aliskiren 75 mg, 150 mg and 300 mg to placebo in patients with essential hypertension. Novartis Clinical Trials Results Database November 4th 2009:1‐14.
-
- Puig JG, Schunkert H, Taylor AA, Boye S, Jin J, Keefe DL. Evaluation of the dose‐response relationship of aliskiren, a direct renin inhibitor in an 8‐week, multicenter, randomized, double‐blind, parallel‐group, placebo‐controlled study in adult patients with stage 1 or 2 essential hypertension. Clinical Therapeutics 2009;31(12):2839‐50. - PubMed
CSPP100A2405 {published data only}
-
- Novartis. An eight‐week double‐blind, multi‐center, randomized, placebo‐controlled, parallel‐group study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of aliskiren 75 mg, 150 mg and 300 mg in elderly patients with essential hypertension when given with a light meal. Clinical Study Report. European Medicines Agency. Date not reported:1‐100.
-
- Villa G, Breton S, Ibram G, Keefe D. Efficacy, safety and tolerability of Aliskiren monotherapy administered with a light meal in elderly hypertensive patients: A randomized, double blind, placebo‐controlled, dose‐response evaluation study. Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 2012;52:1901‐11. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Andersen 2008 {published data only}
-
- Andersen K, Weinberger MH, Egan B, Constance CM, Ali MA, Jin J, et al. Comparative efficacy and safety of aliskiren, an oral direct renin inhibitor, and ramipril in hypertension: A 6‐month, randomized, double‐blind trial. Journal of Hypertension 2008;3:589‐92. - PubMed
Dorresteijn 2013 {published data only}
-
- Dorresteijn JA, Schrover IM, Visseren FL, Scheffer PG, Oey PL, Danser AH, et al. Differential effects of renin‐angiotensin‐aldosterone system inhibition, sympathoinhibition and diuretic therapy on endothelial function and blood pressure in obesity‐related hypertension: a double‐blind, placebo‐controlled cross‐over trial. Journal of Hypertension 2013;31(2):393‐403. - PubMed
Frandesen 2008 {published data only}
-
- Frandsen E, Persson F, Boomsma F, Prescott M, Dole WP, Rossing P, et al. The effect of direct renin inhibition alone or in combination with angiotensin II receptor blockade on markers of the renin‐angiotension aldosterone system. Diabetologica 2008;51(Suppl 1):S 491.
Gheorghiade 2013 {published data only}
-
- Gheorghiade M, Bohm M, Greene SJ, Fonarow GC, Lewis EF, Zannad F, et al. ASTRONAUT Investigators and Coordinators. Effect of aliskiren on postdischarge mortality and heart failure readmissions among patients hospitalized for heart failure: the ASTRONAUT randomized trial.. JAMA 2013 March 20;309(11):1125‐35. - PubMed
Jordan 2007 {published data only}
-
- Jordan J, Engeli S, Boye SW, Breton S, Keefe DL. Direct Renin inhibition with aliskiren in obese patients with arterial hypertension. Hypertension 2007;49(5):1047‐55. - PubMed
Jumar 2015 {published data only}
-
- Jumar A, Ott C, Kistner I, Friedrich S, Schmidt S, Harazny, JM, et al. Effect of aliskiren on vascular remodelling in small retinal circulation. Journal of Hypertension 2015;33(12):2491‐9. - PubMed
Maser 2013 {published data only}
Mihai 2013 {published data only}
-
- Mihai G, Varghese J, Kampfrath T, Gushchina L, Hafer L, Deiuliis, et al. Aliskiren effect on plaque progression in established atherosclerosis using high resolution 3D MRI (ALPINE): a double‐blind placebo‐controlled trial. Journal of the American Heart Association 2013 June;2(3):e004879. - PMC - PubMed
NCT00219141 {published data only}
-
- Novartis. Aliskiren in combination with losartan compared to losartan on the regression of left ventricular hypertrophy in overweight patients with essential hypertension (ALLAY). ClinicalTrials.gov identifier NCT00219141 May 2011:1‐31.
NCT00417170 {published data only}
-
- Novartis. Comparison of aliskiren and amlodipine on insulin resistance and endothelial dysfunction in patients with hypertension and metabolic syndrome. ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier NCT00417170 September 2011:1‐14.
NCT00654875 {published data only}
-
- Novartis NCT00654875. Efficacy and safety of once daily dosing of aliskiren (300 mg (qd) once a day) to twice daily dosing of aliskiren (150 mg (bid) twice a day) in treating moderate hypertension. ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier NCT00654875 June 2011:1‐18.
NCT00777946 {published data only}
-
- Novartis. Study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of combination aliskiren/amlodipine in patients not adequately responding to aliskiren alone. ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier NCT00777946 June 2011:1‐18.
NCT00819767 {published data only}
-
- Novartis. Efficacy and safety of aliskiren in patients with mild to moderate hypertension during exercise. ClinicalTrials.gov identifier NCT00819767 January 2009:1‐13.
NCT00865020 {published data only}
-
- Novartis. Efficacy and safety of aliskiren 300 mg compared to telmisartan 80 mg after 1 week of treatment withdrawal (ASSERTIVE). ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier NCT00865020 June 2011:1‐17.
NCT00927394 {published data only}
-
- Novartis. Aliskiren and valsartan vs valsartan alone in patients with stage ii systolic hypertension and type ii diabetes mellitus. ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier NCT00927394 December 2012:1‐29.
NCT01042392 {published data only}
-
- Novartis. Efficacy of aliskiren compared to ramipril in the treatment of moderate systolic hypertensive patients (ALIAS). ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier NCT01042392 March 2012:1‐26.
NCT01138423 {published data only}
-
- Novartis. Treatment of Adiposity Related hypErTension (TARGET). ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier NCT01138423 February 2012.
NCT01318395 {published data only}
-
- Novartis. Randomized, double blind, active‐controlled, parallel study to analyse effects of the combination of aliskiren and valsartan on the vascular structure and function of retinal vessels. ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier NCT01318395 June 2014.
Nicholls 2013 {published data only}
-
- Nicholls SJ, Bakris GL, Kastelein JJ, Menon V, Williams B, Armbrecht J, et al. Effect of aliskiren on progression of coronary disease in patients with prehypertension: the AQUARIUS randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2013 September 18.;310(11):1135‐44. - PubMed
Nussberger 2007 {published data only}
-
- Nussberger J, Gradman AH, Schmieder RE, LinsRL, Chiang Y, Prescott MF. Plasma renin and the antihypertensive effect of the orally active renin inhibitor aliskiren in clinical hypertension. International Journal ofClinical Practice 2007;61(9):1461‐8. - PubMed
O'Brien 2007 {published data only}
-
- O'Brien E, Barton J, Nussberger J, Mulcahy D, Jensen C, Dicker P, et al. Aliskiren reduces blood pressure and suppresses plasma renin activity in combination with a thiazide diuretic, an angiotensin‐converting enzyme inhibitor, or an angiotensin receptor blocker. Hypertension 2007;49(2):276‐84. - PubMed
Persson 2009 {published data only}
-
- Novartis. Study to assess the optimal renoprotective dose of aliskiren in hypertensive patients with type 2 diabetes and incipient or overt nephropathy. ClinicalTrials.gov identifier NCT00464776 April 2007.
Pitt 2007 {published data only}
-
- Pitt B, McMurray JJ, Latini R, Maggioni A, Solomon SD, Smith BA, et al. Neurohumoral effects of a new oral direct renin inhibitor in stable heart failure: The Aliskiren Observation of Heart Failure Treatment study (ALOFT. Circulation 2007;116(16 Suppl):S.
Scirica 2010 {published data only}
-
- Scirica BM, Morrow DA, Bode C, Ruzyllo W, Ruda M, Oude Ophuis AJ, et al. Patients with acute coronary syndromes and elevated levels of natriuretic peptides: the results of the AVANT GARDE‐TIMI 43 Trial. European Heart Journal 2010 August;31(16):1993‐2005. - PubMed
Shah 2012 {published data only}
-
- Shah AM, Shin SH, Takeuchi M, Skali H, Desai AS, Kober L, et al. Left ventricular systolic and diastolic function, remodelling, and clinical outcomes among patients with diabetes following myocardial infarction and the influence of direct renin inhibition with aliskiren. European Journal of Heart Failure 2012, February;142(2):185‐92. - PubMed
Solomon 2011 {published data only}
-
- Solomon SD, Shin SH, Shah A, Skali H, Desai A, Kober L, et al. Effect of the direct renin inhibitor aliskiren on left ventricular remodelling following myocardial infarction with systolic dysfunction. European Heart Journal 2011;32(10):1227‐34. - PubMed
Stanton 2003 {published data only}
-
- Stanton A, Jensen C, Nussberger J, O'Brien E. Blood pressure lowering in essential hypertension with an oral renin inhibitor, aliskiren. Hypertension 2003;42(6):1137‐43. - PubMed
Strasser 2007 {published data only}
-
- Strasser RH, Puig JG, Farsang C, Croket M, Li J, Ingen H. A comparison of the tolerability of the direct renin inhibitor aliskiren and lisinopril in patients with severe hypertension. Journal of Human Hypertension 2007;21(10):780‐7. - PubMed
Teo 2014 {published data only}
-
- Teo KK, Pfeffer M, Mancia G, O'Donnell M, Dagenais G, Diaz R, et al. Aliskiren Prevention of Later Life Outcomes trial Investigators. Aliskiren alone or with other antihypertensives in the elderly with borderline and stage 1 hypertension: the APOLLO trial. European Heart Journal 2014;35(26):1743‐51. - PMC - PubMed
Uresin 2007 {published data only}
-
- Uresin Y, Taylor AA, Kilo C, Tschope D, Santonastaso M, Ibram G, et al. Efficacy and safety of the direct renin inhibitor aliskiren and ramipril alone or in combination in patients with diabetes and hypertension. Journal of the Renin‐Angiotensin‐Aldosterone System 2007;8(4)(4):190‐8. - PubMed
Verdecchia 2007 {published data only}
-
- Verdecchia P, Calvo C, Mockel V, Keeling L, Satlin A. Safety and efficacy of the oral direct renin inhibitor aliskiren in elderly patients with hypertension. Blood Pressure 2007;16(6):381‐91. - PubMed
Additional references
ALTITUDE 2012
-
- Parving HH, Brenner BM, McMurray JH, Zeeuw D, Haffner SM, Solomon, et al. ALTITUDE Investigators. Cardiorenal end points in a trial of aliskiren for type 2 diabetes. New England Journal of Medicine 2012;367:2204‐13. - PubMed
AQUARIUS 2013
-
- Nicholls SJ, Bakris GL, Kastelein JP, et al. Effect of Aliskiren on Progression of Coronary Disease in Patients With PrehypertensionThe AQUARIUS Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2013;310(11):1135‐44. - PubMed
ASPIRE 2011
-
- Solomon SD, Shin SH, Shah A, Skali H, Desai A, Kober L, Maggioni AP, Rouleau JL, Kelly RY, Hester A, McMurray JJ, Pfeffer MA. Aliskiren Study in Post‐MI Patients to Reduce Remodeling (ASPIRE) Investigators. European Heart Journal May 2011;32:1227‐34. - PubMed
ASTRONAUT 2013
-
- Gheorghiade M, Böhm M, Greene SJ, Fonarow GC, Lewis EF, Zannad F, Solomon SD, Baschiera F, Botha J, Hua TA, Gimpelewicz CR, Jaumont X, Lesogor A, Maggioni AP, ASTRONAUT Investigators and Coordinators. Effect of aliskiren on postdischarge mortality and heart failure readmissions among patients hospitalized for heart failure: the ASTRONAUT randomized trial. JAMA March 20 2013;309(11):1125‐35. - PubMed
AVANT GARDE ‐ TIMI 43 2010
-
- Scirica BM, Morrow DA, Bode C, Ruzyllo W, Ruda M, Oude Ophuis AJ, Lopez‐Sendon J, Swedberg K, Ogorek M, Rifai N, Lukashevich V, Maboudian M, Cannon CP, McCabe CH, Braunwald E. Patients with acute coronary syndromes and elevated levels of natriuretic peptides: the results of the AVANT GARDE‐TIMI 43 Trial. European Heart Journal 2010;31(16):1993‐2005. - PubMed
AVOID 2011
-
- Persson F, Lewis JB, Lewis EJ, Rossing P, Hollenberg NK, Parving HH. Aliskiren in combination with losartan reduces albuminuria independent of baseline blood pressure in patients with type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol May 2011;6(5):1025‐31. [DOI: 10.2215/CJN.07590810] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Chalmers 1990
-
- Chalmers I. Underreporting research is scientific misconduct. JAMA 1990;263(10):1405‐8. - PubMed
Chen 2013
-
- Chen Y, Meng L, Shao H, Feng Yu. Aliskiren vs. other antihypertensive drugs in the treatment of hypertension: a meta‐analysis. Hypertension Research 2013;36:252‐61. - PubMed
Doshi 2012
Doshi 2016
Duprez 2006
-
- Duprez D. Role of the renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system in vascular remodeling and inflammation: a clinical review. Journal of Hypertension 2006;24:983‐91. - PubMed
Dwan 2013
Eyding 2010
FDA Medical Review 2007
-
- Center for drug evaluation and research. Tekturna (Aliskiren) Medical Review. FDA database March 5th 2007, issue Application number 21‐985:1‐283.
Frishman 1994
-
- Frishman WH, Fozailoff A, Lin C, Dike C. Renin inhibition: a new approach to cardiovascular therapy. Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 1994;34:873‐80. - PubMed
Gotzsche 2011
-
- Gotzsche P, Jorgenson AW. Opening up data at the European Medicines Agency. BMJ 2011;343:1184‐6. - PubMed
Gradman 2005
-
- Gradman A, Schmieder R, Lins R, Nussberger J, Chiang Y, Bedigian M. Aliskiren, a novel orally effective renin inhibitor, provides dose‐dependent antihypertensive efficacy and placebo‐like tolerability in hypertensive patients. Circulation 2005;111:1012‐8. - PubMed
Gradman 2010
-
- Gradman AH, Weir MR, Wright M, Bush CA, Keefe DL. Efficacy, safety and tolerability of aliskiren, a direct renin inhibitor, in women with hypertension: a pooled analysis of eight studies. Journal of Human Hypertension 2010;24:721‐9. - PubMed
Harel 2012
-
- Harel Z, Gilbert C, Wald R, Bell C, Perl J, Juurlink D, et al. The effect of combination treatment with aliskiren and blockers of the renin‐angiotensin system on hyperkalaemia and acute kidney injury: systematic review and meta‐analysis. BMJ 2012;344(e42):1‐13. [DOI: 10.1136/bmj.e42] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Hart 2012
-
- Hart 2012. Effect of reporting bias on meta‐analyses of drug trials reanalysis of meta‐analyses. BMJ 2012;344:13. - PubMed
Helmer 1958
-
- Helmer OM. Studies on renin antibodies. Circulation 1958;17(4 part 2):648‐52. - PubMed
Heran 2008a
Heran 2008b
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Version 5.10 [updated March 2011]. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org: The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011.
Hodkinson 2013
Hodkinson 2016
Jefferson 2014
Jefferson 2015
-
- Jefferson T. Facing the unreliability of clinical trials literature. Drug and Therapeutics Bulletin of Navarre, Spain 2015;22(2):1‐11.
Kirkham 2010
-
- Kirkham JJ, Dwan KM, Altman DG, Gamble C, Dodd S, Smyth R, et al. The impact of outcome reporting bias in randomised controlled trials on a cohort of systematic reviews. BMJ 2010;340:637‐40. - PubMed
Krum 2007
-
- Krum H, Gilbert RE. Novel therapies blocking the renin‐angiotensin‐aldosterone system in the management of hypertension and related disorders. Journal of Hypertension 2007;25:25‐35. - PubMed
Kushiro 2006
-
- Kushiro T, Hiroshige I, Yoshihisa A, Hiromi G, Shinji T, Keefe D. Aliskiren, a novel oral renin inhibitor, provides dose‐dependent efficacy and placebo‐like tolerability in Japanese patients with hypertension. Hypertension Research ‐ Clinical & Experimental 2006;29(12):997‐1005. - PubMed
Law 2003
Littlejohn 2013
-
- Littlejohn TW 3rd, Jones SW, Zhang J, Hsu H, Keefe DL. Efficacy and safety of aliskiren and amlodipine combination therapy in patients with hypertension: a randomized, double‐blind, multifactorial study. Journal of Human Hypertension 2013;27(5):321‐7. - PubMed
Makani 2013
Maund 2014
McGauran 2010
Musini 2009
Novartis Clinical Trial Results Database
-
- Novartis. Novartis Clinical Trials Database https://www.novartisclinicaltrials.com/TrialConnectWeb/home.nov.
Oh 2007
-
- Oh B, Mitchell J, Herron J, Chung J, Khan Ml, Keefe D. Aliskiren, an oral renin inhibitor, provides dose‐dependent efficacy and sustained 24‐hour blood pressure control in patients with hypertension. Journal of the Amarican College of Cardiology 2007;49(11):1157‐63. - PubMed
Oparil 2007
-
- Oparil S, Yarrows S, Patel SF, Ang H, Zhang J, Satlin A. Efficacy and safety of combined use of aliskiren and valsartan in patients with hypertension: a randomised, double‐blind trial. Lancet 2007;370(9583):221‐9. - PubMed
Pool 2007
-
- Pool J, Roland E, Schmieder M, Aldigier JC, Januszewicz A, Zidek W, Chiang Y, Satlin A. Aliskiren, an orally effective renin inhibitor, provides antihypertensive efficacy alone and in combination with valsartan. American Journal of Hypertension 2007;20(1):11‐20. - PubMed
Poulter 2015
-
- Poulter NR, Prabhakaran D, Caulfield M. Hypertension. Lancet 22nd August 2015;386(9995):801‐12. - PubMed
Powers 2011
-
- Powers B, Greene L, Balfe LM. Updates on the treatment of essential hypertension: a summary of AHRQ's comparativeeffectiveness review of angiotensin‐converting enzyme inhibitors, angiotensin II receptorblockers, and direct renin inhibitors. Journal of Managed Care Pharmacy October 2011;17(8):Supplement S1‐S14. - PMC - PubMed
Puig 2009
-
- Puig JG, Schunkert H, Taylor AA, Boye S, Jin J, Keefe DL. Evaluation of the dose‐response relationship of aliskiren, a direct renin inhibitor in an 8‐week, multicenter, randomized, double‐blind, parallel‐group, placebo‐controlled study in adult patients with stage 1 or 2 essential hypertension. Clinical Therapeutics 2009;31(12):2839‐50. - PubMed
Rising 2008
Schmieder 2009
-
- Schmieder RE, Philipp T, Guerediaga J, Gorostidi M, Smith B, Weissbach N, et. al. Long‐term antihypertensive efficacy and safety of the Oral direct renin Inhibitor aliskiren. Circulation 2009;119:417‐25. - PubMed
Schünemann 2011
-
- Schünemann HJ, Oxman AD, Vist GE, Higgins JPT, Deeks Jj, Glasziou P, et al. Chapter 12: Interpreting results and drawing conclusions. In: Higgins JPT, Green S editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org: The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011.
Sharma 2016
U.S. Food and Drug Administration 2016
-
- FDA Drug Safety Communication: New Warning and Contraindication for blood pressure medicines containing aliskiren (Tekturna). http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/DrugSafety/ucm300889.htm#data Last updated on19th January 2016.
Villa 2012
-
- Villa G, Breton S, Ibram G, Keefe D. Efficacy, safety and tolerability of Aliskiren monotherapy administered with a light meal in elderly hypertensive patients: A randomized, double blind, placebo‐controlled, dose‐response evaluation study. Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 2012;52:1901‐11. - PubMed
Villamil 2007
-
- Villamil A, Chrysant S, Calhoun D, Schober B, Hsu H, Matrisciano‐Dimichino L, Zhang J. Renin inhibition with aliskiren provides additive antihypertensive efficacy when used in combination with hydrochlorothiazide. Journal of hypertension 2007;25(1):217‐226. - PubMed
Weir 2007
-
- Weir MR, Bush C, Anderson DR, Zhang J, Keefe D, Satlin A. Antihypertensive efficacy, safety, and tolerability of the oral direct renin inhibitor aliskiren in patients with hypertension: a pooled analysis. Journal of the American Society of Hypertension 2007;1(4):264‐77. - PubMed
White 2010
Wieseler 2012
-
- Wieseler B, Chrysant SG, Calhoun D, Schober B, Hsu H, Matrisciano‐Dimichino L, et al. Impact of document type on reporting ality of clinical drug trials: a comparison of registry reports, clinical study reports, and journal publications. BMJ 2012;344:1‐11. - PubMed
Wright 2009
References to other published versions of this review
Musini 2009
-
- Musini VM, Fortin PM, Bassett K, Wright JM. Blood pressure lowering efficacy of renin inhibitors for primary hypertension:a Cochrane systematic review. Journal of Human Hypertension 2009;23(8):495‐502. - PubMed
Musini 2008a
Musini 2008b
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

