Randomized controlled trial of a home-based palliative approach for people with severe multiple sclerosis
- PMID: 28381133
- PMCID: PMC5946675
- DOI: 10.1177/1352458517704078
Randomized controlled trial of a home-based palliative approach for people with severe multiple sclerosis
Abstract
Background: Evidence on the efficacy of palliative care in persons with severe multiple sclerosis (MS) is scarce.
Objective: To assess the efficacy of a home-based palliative approach (HPA) for adults with severe MS and their carers.
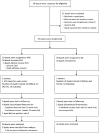
Methods: Adults with severe MS-carer dyads were assigned (2:1 ratio) to either HPA or usual care (UC). At each center, a multi-professional team delivered the 6-month intervention. A blind examiner assessed dyads at baseline, 3 months, and 6 months. Primary outcome measures were Palliative care Outcome Scale-Symptoms-MS (POS-S-MS) and Schedule for the Evaluation of Individual Quality of Life-Direct Weighting (SEIQoL-DW, not assessed in severely cognitively compromised patients).
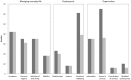
Results: Of 78 dyads randomized, 76 (50 HPA, 26 UC) were analyzed. Symptom burden (POS-S-MS) significantly reduced in HPA group compared to UC ( p = 0.047). Effect size was 0.20 at 3 months and 0.32 at 6 months, and statistical significance was borderline in per-protocol analysis ( p = 0.062). Changes in SEIQoL-DW index did not differ in the two groups, as changes in secondary patient and carer outcomes.
Conclusion: HPA slightly reduced symptoms burden. We found no evidence of HPA efficacy on patient quality of life and on secondary outcomes.
Keywords: Multiple sclerosis; caregivers; palliative care; quality of life; randomized controlled trial; symptom burden.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Lublin FD, Reingold SC. Defining the clinical course of multiple sclerosis: Results of an international survey. Neurology 1996; 46: 907–911. - PubMed
-
- NICE. Multiple sclerosis in adults: Management (CG186). London: NICE, 2014.
-
- Edmonds P, Hart S, Wei G, et al. Palliative care for people severely affected by multiple sclerosis: Evaluation of a novel palliative care service. Mult Scler 2010; 16: 627–636. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

