Melamine induces Ca2+-sensing receptor activation and elicits apoptosis in proximal tubular cells
- PMID: 28381520
- PMCID: PMC5538798
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpcell.00225.2016
Melamine induces Ca2+-sensing receptor activation and elicits apoptosis in proximal tubular cells
Abstract
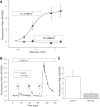
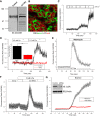
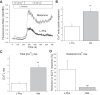
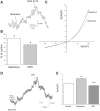
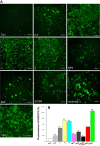
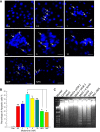
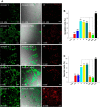
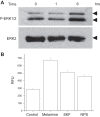
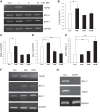
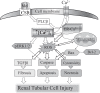
Melamine causes renal tubular cell injury through inflammation, fibrosis, and apoptosis. Although melamine affects the rise in intracellular Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i), reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, and proapoptotic pathway activation, the mechanism of upstream Ca2+ signaling is unknown. Because melamine has some structural similarities with l-amino acids, which endogenously activate Ca2+-sensing receptors (CSR), we examined the effect of melamine on CSR-induced Ca2+ signaling and apoptotic cell death. We show here that melamine activates CSR, causing a sustained Ca2+ entry in the renal epithelial cell line, LLC-PK1. Moreover, such CSR stimulation resulted in a rise in [Ca2+]i, leading to enhanced ROS production. Furthermore, melamine-induced elevated [Ca2+]i and ROS production caused a dose-dependent increase in apoptotic (by DAPI staining, DNA laddering, and annexin V assay) and necrotic (propidium iodide staining) cell death. Upon examining the downstream mechanism, we found that transforming growth factor β1 (TGF-β1), which increases extracellular matrix genes and proapoptotic signaling, was also upregulated at lower doses of melamine, which could be due to an early event inducing apoptosis. Additionally, cells exposed to melamine displayed a rise in pERK activation and lactate dehydrogenase release resulting in cytotoxicity. These results offer a novel insight into the molecular mechanisms by which melamine exerts its effect on CSR, causing a sustained elevation of [Ca2+]i, leading to ROS generation, fibronectin production, proapoptotic pathway activation, and renal cell damage. Together, these results thus suggest that melamine-induced apoptosis and/or necrosis may subsequently result in acute kidney injury and promote kidney stone formation.
Keywords: Ca2+-sensing receptor; acute kidney injury; apoptosis; cell cytotoxicity; intracellular Ca2+; kidney stone; kidney tubular cells; melamine.
Figures
References
-
- Bahar E, Lee GH, Bhattarai KR, Lee HY, Choi MK, Rashid HO, Kim JY, Chae HJ, Yoon H. Polyphenolic extract of euphorbia supina attenuates manganese-induced neurotoxicity by enhancing antioxidant activity through regulation of ER stress and ER stress-mediated apoptosis. Int J Mol Sci 18: E300, 2017. doi:10.3390/ijms18020300. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

