Effects of 12 Weeks Resistance Training on Serum Irisin in Older Male Adults
- PMID: 28382004
- PMCID: PMC5360699
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2017.00171
Effects of 12 Weeks Resistance Training on Serum Irisin in Older Male Adults
Abstract
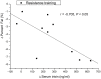
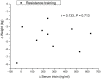
Background: To assess the effects of resistance training on circulating irisin concentration in older male adults, and to investigate the association between resistance training induced alteration of irisin and body fat. Methods: Seventeen older adults (mean age is 62.1 years old) were randomized into old control group (male, n = 7), and old training group (male, n = 10). The control group has no any exercise intervention. The resistance training group underwent leg muscle strength and core strength training program two times/wk, 55 min/class for 12 weeks. Before and after the intervention, we evaluated serum irisin level and body composition. Results: Serum irisin level was significantly increased in the resistance training group after the 12 weeks intervention period (P < 0.01), but not in the control group. In the resistance training group, the reduction in whole-body fat percent was negatively correlated with the increase in serum irisin level (r = -0.705, P < 0.05). Conclusion: After the 12 weeks intervention, circulating irisin levels were significantly elevated in the older adults. In summary, serum irisin may be involved in the regulation of body fat in older male adults.
Keywords: body fat; dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA); irisin; resistance training; skin fold.
Figures
References
-
- Huh J. Y., Panagiotou G., Mougios V., Brinkoetter M., Vamvini M. T., Schneider B. E., et al. (2012). FNDC5 and irisin in humans: I. Predictors of circulating concentrations in serum and plasma and II. mRNA expression and circulating concentrations in response to weight loss and exercise. Metabolism 61, 1725–1738. 10.1016/j.metabol.2012.09.002 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources