NR1H3 Expression is a Prognostic Factor of Overall Survival for Patients with Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer
- PMID: 28382148
- PMCID: PMC5381174
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.17845
NR1H3 Expression is a Prognostic Factor of Overall Survival for Patients with Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer
Abstract
Background: Nuclear receptors (NRs) are a class of transcription factors that regulate many cellular functions through manipulation of gene expression and also play important roles in tumorigenesis, proliferation, progression and prognosis in various kinds of cancers according to recent studies. This work aimed to determine the predictive ability of NRs in muscle-invasive bladder cancer (MIBC).
Patients and methods: A total of 308 MIBC patients with complete clinicopathological and RNASeq data from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) cohort were collected for filtration. Genes showed clear correlations with overall survival (OS) and recurrence free survival (RFS) were further validated in 123 MIBC patients recruited consecutively from 2008 to 2012 in Fudan University Shanghai Cancer Center (FUSCC) cohort. Cox proportional hazards regression model and Kaplan-Meier plot were used to assess the relative factors.
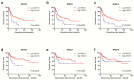
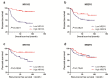
Results: In TCGA cohort, we found that high NR1H3 (HR=0.779, 95% CI: 0.634 - 0.957), NR2C1 (HR=0.673, 95% CI: 0.458 - 0.989) and NR2F6 (HR=0.750, 95% CI: 0.574 - 0.980) expressions were independent factors of favorable OS, while only low NR1H3 (log-rank test, P=0.0076) and NR2F6 (log-rank test, P=0.0395) expressions had the ability to predict poor prognosis for RFS. Further, in FUSCC validating cohort, we confirmed that low NR1H3 expression level was independent factor of poor OS (HR=1.295, 95% CI: 1.064 - 1.576) and it had the ability to predict poor RFS (log-rank test, P=0.0059).
Conclusions: Low NR1H3 expression level is an independent prognostic factor of poor OS, and can also predict worse RFS in MIBC patients. Our "TCGA filtrating and local database validating" model can help reveal more prognostic biomarkers and cast a new light in understanding certain gene function in MIBC.
Keywords: NR1H3; Nuclear receptor; muscle-invasive bladder cancer; overall survival.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
References
-
- Abdollah F, Gandaglia G, Thuret R, Schmitges J, Tian Z, Jeldres C. et al. Incidence, survival and mortality rates of stage-specific bladder cancer in United States: a trend analysis. Cancer epidemiology. 2013;37:219–25. - PubMed
-
- Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng H, Bray F. et al. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA: a cancer journal for clinicians. 2016;66:115–32. - PubMed
-
- Rocken C, Behrens HM. Validating the prognostic and discriminating value of the TNM-classification for gastric cancer - a critical appraisal. European journal of cancer (Oxford, England: 1990) 2015;51:577–86. - PubMed
-
- Sobin L H GM, Wittekind C. TNM classification of malignant tumours (Uicc international union against cancer) 7th ed ed; 2009.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

