Enhancement of cytokine-driven NK cell IFN-γ production after vaccination of HCMV infected Africans
- PMID: 28383105
- PMCID: PMC5888140
- DOI: 10.1002/eji.201746974
Enhancement of cytokine-driven NK cell IFN-γ production after vaccination of HCMV infected Africans
Abstract
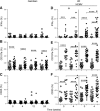
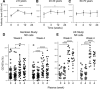
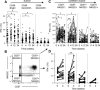
Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) infection drives the phenotypic and functional differentiation of NK cells, thereby influencing the responses of these cells after vaccination. NK cell functional differentiation is particularly advanced in African populations with universal exposure to HCMV. To investigate the impact of advanced differentiation on vaccine-induced responses, we studied NK-cell function before and after vaccination with Trivalent Influenza Vaccine (TIV) or diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, inactivated poliovirus vaccine (DTPiP) in Africans with universal, lifelong HCMV exposure. In contrast to populations with lower prevalence of HCMV infection, no significant enhancement of NK-cell responses (IFN-γ, CD107a, CD25) occurred after in vitro re-stimulation of post-vaccination NK cells with TIV or DTPiP antigens compared to pre-vaccination baseline cells. However, both vaccinations resulted in higher frequencies of NK cells producing IFN-γ in response to exogenous IL-12 with IL-18, which persisted for up to 6 months. Enhanced cytokine responsiveness was restricted to less differentiated NK cells, with increased frequencies of IFN-γ+ cells observed within CD56bright CD57- , CD56dim CD57- NKG2C- and CD56dim CD57- NKG2C+ NK-cell subsets. These data suggest a common mechanism whereby different vaccines enhance NK cell IFN-γ function in HCMV infected donors and raise the potential for further exploitation of NK cell "pre-activation" to improve vaccine effectiveness.
Keywords: DTPiP vaccine; Influenza vaccine; NK cells; NKG2C; Vaccination.
© 2017 The Authors. European Journal of Immunology published by WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures


References
-
- Kiessling, R. , Klein, E. , Pross, H. and Wigzell, H. , “Natural” killer cells in the mouse. II. Cytotoxic cells with specificity for mouse Moloney leukemia cells. Characteristics of the killer cell. Eur. J. Immunol. 1975. 5: 117–121. - PubMed
-
- Fehniger, T. A. , Cooper, M. A. , Nuovo, G. J. , Cella, M. , Facchetti, F. , Colonna, M. and Caligiuri, M. A. , CD56bright natural killer cells are present in human lymph nodes and are activated by T cell‐derived IL‐2: a potential new link between adaptive and innate immunity. Blood 2003. 101: 3052–3057. - PubMed
-
- Horowitz, A. , Behrens, R. H. , Okell, L. , Fooks, A. R. and Riley, E. M. , NK cells as effectors of acquired immune responses: effector CD4+ T cell‐dependent activation of NK cells following vaccination. J. Immunol. 2010. 185: 2808–2818. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

