Can auscultatory blood pressure normative values be used for evaluation of oscillometric blood pressure in children?
- PMID: 28383188
- PMCID: PMC8031177
- DOI: 10.1111/jch.12943
Can auscultatory blood pressure normative values be used for evaluation of oscillometric blood pressure in children?
Abstract
The aim of the study was to analyze whether auscultatory normative values (Fourth Task Force [4TF]) can be applied to blood pressure (BP) obtained by oscillometric devices. The authors performed a retrospective analysis of oscillometric office BP and ambulatory BP monitoring in 229 children (116 boys), median age 15.31 years. Office systolic BP (SBP) and diastolic BP (DBP) values were converted into Z scores using 4TF and oscillometric (German Health Interview and Examination Survey for Children and Adolescent [KiGGS]) reference values. There was good correlation between the two normative methods (r=0.9773 for SBP, r=0.9627 for DBP). Results from Bland-Altman test revealed only minimal differences in Z scores between 4TF and KiGGS for SBP, but a significant proportional error for DBP. 4TF and KiGGS Z scores were equally predictive of ambulatory hypertension. In conclusion, auscultatory and oscillometric normative data are interchangeable for SBP but not for DBP.
Keywords: auscultatory normative values; blood pressure; children; oscillometric normative values.
©2016 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have nothing to disclose nor have any competing financial interest in relation to the work described.
Figures
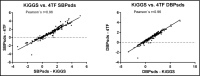

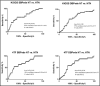
Similar articles
-
Reliability of resting blood pressure measurement and classification using an oscillometric device in children with chronic kidney disease.J Pediatr. 2012 Mar;160(3):434-440.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2011.08.071. Epub 2011 Nov 1. J Pediatr. 2012. PMID: 22048052 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison between oscillometric and auscultatory methods of ambulatory blood pressure measurement in hemodialysis patients.Clin Nephrol. 2002 Apr;57(4):283-8. doi: 10.5414/cnp57283. Clin Nephrol. 2002. PMID: 12005244
-
Auscultatory versus oscillometric measurement of blood pressure in octogenarians.Blood Press. 2012 Oct;21(5):269-72. doi: 10.3109/08037051.2012.680751. Epub 2012 May 1. Blood Press. 2012. PMID: 22545576
-
Blood pressure, hypertension, and ambulatory blood pressure monitoring in children and adolescents.Am J Hypertens. 2002 Feb;15(2 Pt 2):64S-66S. doi: 10.1016/s0895-7061(01)02307-x. Am J Hypertens. 2002. PMID: 11866234 Review.
-
Blood pressure measurement: retrospective and prospective views.Am J Hypertens. 2011 Jun;24(6):628-34. doi: 10.1038/ajh.2011.22. Epub 2011 Feb 24. Am J Hypertens. 2011. PMID: 21350431 Review.
Cited by
-
Blood pressure is normal, but is the heart?Pediatr Nephrol. 2018 Sep;33(9):1585-1591. doi: 10.1007/s00467-018-3968-5. Epub 2018 May 15. Pediatr Nephrol. 2018. PMID: 29766272
-
Hypertension in obese children is associated with vitamin D deficiency and serotonin dysregulation.BMC Pediatr. 2022 May 17;22(1):289. doi: 10.1186/s12887-022-03337-8. BMC Pediatr. 2022. PMID: 35581625 Free PMC article.
-
The population-based prevalence of hypertension and correlates of blood pressure among Australian children.Pediatr Nephrol. 2019 Jun;34(6):1107-1115. doi: 10.1007/s00467-019-04206-w. Epub 2019 Feb 18. Pediatr Nephrol. 2019. PMID: 30778829
References
-
- Chobanian AV, Bakris GL, Black HR, et al. National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure; National High Blood Pressure Education Program Coordinating Committee . The Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure: the JNC 7 report. JAMA. 2003;289:2560–2572. - PubMed
-
- Mancia G, De Backer G, Dominiczak A, et al. Management of Arterial Hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension; European Society of Cardiology. 2007 Guidelines for the Management of Arterial Hypertension: The Task Force for the Management of Arterial Hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). J Hypertens. 2007;25:1105–1187. - PubMed
-
- National High Blood Pressure Education Program Working Group on High Blood Pressure in Children and Adolescents . The fourth report on the diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment of high blood pressure in children and adolescents. Pediatrics. 2004;114(2 suppl 4th report): 555–576. - PubMed
-
- Lurbe E, Cifkova R, Cruickshank JK, et al. European Society of Hypertension. Management of high blood pressure in children and adolescents: Recommendations of the European Society of Hypertension. J Hypertens. 2009;27:1719–1742. - PubMed
-
- O'Brien E, Pickering T, Asmar R, et al. Working Group on Blood Pressure Monitoring of the European Society of Hypertension. Working Group on Blood Pressure Monitoring of the European Society of Hypertension International Protocol for validation of blood pressure measuring devices in adults. Blood Press Monit. 2002;7:3–17. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

