Association between fibromyalgia syndrome and peptic ulcer disease development
- PMID: 28384332
- PMCID: PMC5383298
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0175370
Association between fibromyalgia syndrome and peptic ulcer disease development
Abstract
Purpose: The correlation of fibromyalgia syndrome (FMS) with peptic ulcer disease (PUD) is unclear. We therefore conducted a cohort study to investigate whether FMS is correlated with an increased risk of PUD.
Methods: In this study, we established an FMS cohort comprising 26068 patients aged more than 20 years who were diagnosed with FMS from 2000 to 2011. Furthermore, we established a control cohort by randomly choosing 104269 people without FMS who were matched to the FMS patients by gender, age, and index year. All patients were free of PUD at the baseline. Cox proportional hazard regressions were performed to compute the hazard ratio of PUD after adjustment for demographic characteristics and comorbidities.
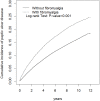
Results: The prevalence of comorbidities was significantly higher in the FMS patients than in the controls. The incidence of PUD was 29.8 and 19.4 per 1000 person-years in the FMS and control cohorts, respectively. In addition, the FMS cohort exhibited a 1.40-fold higher risk of PUD (95% confidence interval = 1.35-1.45) compared with the control cohort. After control for confounding factors, the medications (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors, and antidepressants) taken by the FMS patients did not increase the risk of PUD.
Conclusion: FMS patients exhibit a higher risk of PUD than that of patients without FMS.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Increased incidence of herpes zoster in adult patients with peptic ulcer disease: a population-based cohort study.Int J Epidemiol. 2013 Dec;42(6):1873-81. doi: 10.1093/ije/dyt213. Int J Epidemiol. 2013. PMID: 24536094
-
Seborrheic dermatitis and risk of incident peptic ulcer disease: A nationwide population-based cohort study.Australas J Dermatol. 2021 Nov;62(4):e546-e553. doi: 10.1111/ajd.13680. Epub 2021 Aug 9. Australas J Dermatol. 2021. PMID: 34370301
-
Increased Risk of Osteoporosis in Patients With Peptic Ulcer Disease: A Nationwide Population-Based Study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2016 Apr;95(16):e3309. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000003309. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016. PMID: 27100415 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Increased risk of osteoporosis in patients with peptic ulcer: a follow-up study using a national sample cohort.Arch Osteoporos. 2019 Oct 29;14(1):105. doi: 10.1007/s11657-019-0659-1. Arch Osteoporos. 2019. PMID: 31659478
-
Peptic Ulcer Disease is Associated with Increased Risk of Chronic Urticaria Independent of Helicobacter pylori Infection: A Population-Based Cohort Study.Am J Clin Dermatol. 2021 Jan;22(1):129-137. doi: 10.1007/s40257-020-00561-9. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2021. PMID: 32915422
Cited by
-
Insomnia Increases Symptom Severity and Health Care Utilization in Patients With Fibromyalgia: A Population-based Study.Clin J Pain. 2019 Sep;35(9):780-785. doi: 10.1097/AJP.0000000000000738. Clin J Pain. 2019. PMID: 31268891 Free PMC article.
-
Comorbid and co-occurring conditions in migraine and associated risk of increasing headache pain intensity and headache frequency: results of the migraine in America symptoms and treatment (MAST) study.J Headache Pain. 2020 Mar 2;21(1):23. doi: 10.1186/s10194-020-1084-y. J Headache Pain. 2020. PMID: 32122324 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Erin Lawson, Marks Wallace. Fibromyalgia: clinical guideline and treatments. ISBN-978-3-319-15820-4 (eBook), Springer International publishing Switzerland 2015. pp1-192.
-
- Stisi S, Cazzola M, Buskila D, Spath M, Giamberardino MA, Sarzi-Puttini P, et al. Etiopathogenetic mechanisms of fibromyalgia syndrome. Reumatismo. 2008;60:25–35. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous