Design, synthesis and evaluation of 18F-labeled cationic carbonic anhydrase IX inhibitors for PET imaging
- PMID: 28385087
- PMCID: PMC6445240
- DOI: 10.1080/14756366.2017.1308928
Design, synthesis and evaluation of 18F-labeled cationic carbonic anhydrase IX inhibitors for PET imaging
Abstract
Carbonic anhydrase IX (CA-IX) is a marker for tumor hypoxia, and its expression is negatively correlated with patient survival. CA-IX represents a potential target for eliminating hypoxic cancers. We synthesized fluorinated cationic sulfonamide inhibitors 1-3 designed to target CA-IX. The binding affinity for CA-IX ranged from 0.22 to 0.96 μM. We evaluated compound 2 as a diagnostic PET imaging agent. Compound 2 was radiolabeled with 18F in 10 ± 4% decay-corrected radiochemical yield with 85.1 ± 70.3 GBq/μmol specific activity and >98% radiochemical purity. 18F-labeled 2 was stable in mouse plasma at 37 °C after 1 h incubation. PET/CT imaging was conducted at 1 h post-injection in a human colorectal cancer xenograft model. 18F-labeled 2 cleared through hepatobiliary and renal pathways. Tumor uptake was approximately 0.41 ± 0.06% ID/g, with a tumor-to-muscle ratio of 1.99 ± 0.25. Subsequently, tumor xenografts were visualized with moderate contrast. This study demonstrates the use of a cationic motif for conferring isoform selectively for CA-IX imaging agents.
Keywords: Carbonic anhydrase IX; fluorine-18; molecular imaging; positron emission tomography.
Figures


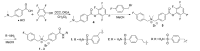





Similar articles
-
Trimeric Radiofluorinated Sulfonamide Derivatives to Achieve In Vivo Selectivity for Carbonic Anhydrase IX-Targeted PET Imaging.J Nucl Med. 2015 Sep;56(9):1434-40. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.114.153288. Epub 2015 Jul 23. J Nucl Med. 2015. PMID: 26205302
-
PET Imaging of Carbonic Anhydrase IX Expression of HT-29 Tumor Xenograft Mice with (68)Ga-Labeled Benzenesulfonamides.Mol Pharm. 2016 Mar 7;13(3):1137-46. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.5b00934. Epub 2016 Feb 19. Mol Pharm. 2016. PMID: 26866675
-
Synthesis and evaluation of (18)F-labeled tertiary benzenesulfonamides for imaging carbonic anhydrase IX expression in tumours with positron emission tomography.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2014 Jul 15;24(14):3064-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2014.05.021. Epub 2014 May 17. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2014. PMID: 24878197
-
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors as emerging agents for the treatment and imaging of hypoxic tumors.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2018 Dec;27(12):963-970. doi: 10.1080/13543784.2018.1548608. Epub 2018 Nov 22. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2018. PMID: 30426805 Review.
-
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors: a review on the progress of patent literature (2011-2016).Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2016 Aug;26(8):947-56. doi: 10.1080/13543776.2016.1203904. Epub 2016 Jul 11. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2016. PMID: 27387065 Review.
Cited by
-
Experimental Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors for the Treatment of Hypoxic Tumors.J Exp Pharmacol. 2020 Dec 15;12:603-617. doi: 10.2147/JEP.S265620. eCollection 2020. J Exp Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 33364855 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative evaluation of affibody- and antibody fragments-based CAIX imaging probes in mice bearing renal cell carcinoma xenografts.Sci Rep. 2019 Oct 17;9(1):14907. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-51445-w. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31624303 Free PMC article.
-
PET imaging and pharmacological therapy targeting carbonic anhydrase-IX high-expressing tumors using US2 platform based on bivalent ureidosulfonamide.PLoS One. 2020 Dec 9;15(12):e0243327. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0243327. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 33296398 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphonamidates are the first phosphorus-based zinc binding motif to show inhibition of β-class carbonic anhydrases from bacteria, fungi, and protozoa.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2020 Dec;35(1):59-64. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2019.1681987. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 31663383 Free PMC article.
-
Past, Present, and Future: Development of Theranostic Agents Targeting Carbonic Anhydrase IX.Theranostics. 2017 Sep 26;7(17):4322-4339. doi: 10.7150/thno.21848. eCollection 2017. Theranostics. 2017. PMID: 29158829 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Vaupel P, Mayer A.. Hypoxia in cancer: significance and impact on clinical outcome. Cancer Metastasis Rev 2007;26:225–39. - PubMed
-
- Wilson WR, Hay MP.. Targeting hypoxia in cancer therapy. Nature Rev Cancer 2011;11:393–410. - PubMed
-
- Brown JM.Tumor hypoxia in cancer therapy. Meth Enzymol 2007;435:297–321. - PubMed
-
- Potter C, Harris AL.. Hypoxia inducible carbonic anhydrase IX, marker of tumour hypoxia, survival pathway and therapy target. Cell Cycle 2004;3:164–7. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
