Free actin impairs macrophage bacterial defenses via scavenger receptor MARCO interaction with reversal by plasma gelsolin
- PMID: 28385809
- PMCID: PMC5495953
- DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.00067.2017
Free actin impairs macrophage bacterial defenses via scavenger receptor MARCO interaction with reversal by plasma gelsolin
Abstract
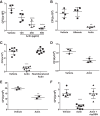
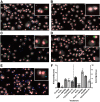
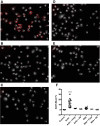
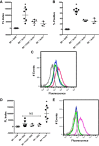
Lung injury can release intracellular actin into the alveolar milieu and is also associated with increased susceptibility to secondary infections. We investigated the effect of free (extracellular) actin on lung macrophage host defense functions. Western blot analysis demonstrated free actin release into the lung lavage fluids of mouse models of ozone injury, influenza infection, and secondary pneumococcal pneumonia and in samples from patients following burn and inhalation injury. Using levels comparable with those observed in lung injury, we found that free actin markedly inhibited murine lung macrophage binding and uptake in vitro of S. pneumoniae, S. aureus, and E. coli, (e.g., S. pneumoniae, mean %inhibition, actin vs. vehicle: 85 ± 0.3 (SD); n = 22, P < .001). Similar effects were observed on the ability of primary human macrophages to bind and ingest fluorescent Saureus (~75% inhibition). Plasma gelsolin (pGSN), a protein that functions to bind and cleave actin, restored bacterial binding and uptake by both murine and human macrophages. Scavenger receptor inhibitors reduced binding of fluorescent actin by murine macrophages [fluorescence index (×10-3) after incubation with vehicle, actin, or actin + polyinosinic acid, respectively: 0.8 ± 0.7, 101.7 ± 50.7, or 52.7 ± 16.9; n = 5-6, P < 0.05]. In addition, actin binding was reduced in a MARCO/SR-AI/II-deficient cell line and by normal AMs obtained from MARCO-/- mice. After release from injured cells during lung injury, free actin likely contributes to impaired host defense by blocking scavenger receptor binding of bacteria. This mechanism for increased risk of secondary infections after lung injury or inflammation may represent another target for therapeutic intervention with pGSN.
Keywords: actin; alveolar macrophages; plasma gelsolin; scavenger receptors.
Copyright © 2017 the American Physiological Society.
Figures

References
-
- Al Ashry HS, Mansour G, Kalil AC, Walters RW, Vivekanandan R. Incidence of ventilator associated pneumonia in burn patients with inhalation injury treated with high frequency percussive ventilation versus volume control ventilation: A systematic review. Burns 42: 1193–1200, 2016. doi: 10.1016/j.burns.2016.02.024. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chang DW, Hayashi S, Gharib SA, Vaisar T, King ST, Tsuchiya M, Ruzinski JT, Park DR, Matute-Bello G, Wurfel MM, Bumgarner R, Heinecke JW, Martin TR. Proteomic and computational analysis of bronchoalveolar proteins during the course of the acute respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 178: 701–709, 2008. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200712-1895OC. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

