Pharmacological Sirt6 inhibition improves glucose tolerance in a type 2 diabetes mouse model
- PMID: 28386046
- PMCID: PMC6137498
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.201601294R
Pharmacological Sirt6 inhibition improves glucose tolerance in a type 2 diabetes mouse model
Abstract
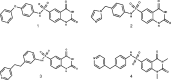
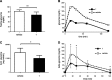
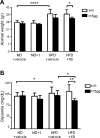
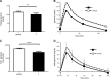
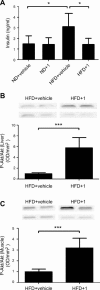
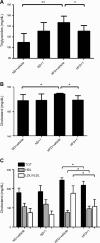
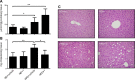
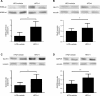
Sirtuin 6 (SIRT6) is a sirtuin family member involved in a wide range of physiologic and disease processes, including cancer and glucose homeostasis. Based on the roles played by SIRT6 in different organs, including its ability to repress the expression of glucose transporters and glycolytic enzymes, inhibiting SIRT6 has been proposed as an approach for treating type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). However, so far, the lack of small-molecule Sirt6 inhibitors has hampered the conduct of in vivo studies to assess the viability of this strategy. We took advantage of a recently identified SIRT6 inhibitor, compound 1, to study the effect of pharmacological Sirt6 inhibition in a mouse model of T2DM (i.e., in high-fat-diet-fed animals). The administration of the Sirt6 inhibitor for 10 d was well tolerated and improved oral glucose tolerance, it increased the expression of the glucose transporters GLUT1 and -4 in the muscle and enhanced the activity of the glycolytic pathway. Sirt6 inhibition also resulted in reduced insulin, triglycerides, and cholesterol levels in plasma. This study represents the first in vivo study of a SIRT6 inhibitor and provides the proof-of-concept that targeting SIRT6 may be a viable strategy for improving glycemic control in T2DM.-Sociali, G., Magnone, M., Ravera, S., Damonte, P., Vigliarolo, T., Von Holtey, M., Vellone, V. G., Millo, E., Caffa, I., Cea, M., Parenti, M. D., Del Rio, A., Murone, M., Mostoslavsky, R., Grozio, A., Nencioni, A., Bruzzone S. Pharmacological Sirt6 inhibition improves glucose tolerance in a type 2 diabetes mouse model.
Keywords: glucose metabolism; glucose transporters; sirtuin inhibitors.
© FASEB.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors thank Thierry Dupraz and Yogeshwar Bacchav (Debiopharm International SA) for technical support. G.S. is a recipient of a fellowship for young investigators granted by Collegio Ghislieri (Pavia, Italy). This work was supported by the Italian Ministry of Health Grant GR-2011–02347192 (to A.N., A.G., and A.D.R.); the University of Genova (to S.B. and A.N.); Programme FP7 PANACREAS Grant 256986 (to A.N. and S.B.) and Athero-B-Cell, Grant 602114 (to A.N.); Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro (AIRC) Grant 17736 (to A.N.); and the Fondazione Umberto Veronesi (to A.N.). G.S. and M.M. contributed equally to this work as first authors. A.N. and S.B. contributed equally to this work as senior authors. The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Nolan C. J., Damm P., Prentki M. (2011) Type 2 diabetes across generations: from pathophysiology to prevention and management. Lancet , 169–181 - PubMed
-
- Liszt G., Ford E., Kurtev M., Guarente L. (2005) Mouse Sir2 homolog SIRT6 is a nuclear ADP-ribosyltransferase. J. Biol. Chem. , 21313–21320 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

