Delivery of ENaC siRNA to epithelial cells mediated by a targeted nanocomplex: a therapeutic strategy for cystic fibrosis
- PMID: 28386087
- PMCID: PMC5428798
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-00662-2
Delivery of ENaC siRNA to epithelial cells mediated by a targeted nanocomplex: a therapeutic strategy for cystic fibrosis
Abstract
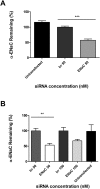
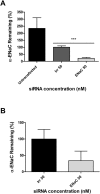
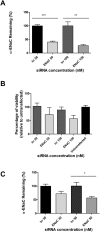
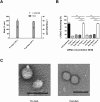
The inhibition of ENaC may have therapeutic potential in CF airways by reducing sodium hyperabsorption, restoring lung epithelial surface fluid levels, airway hydration and mucociliary function. The challenge has been to deliver siRNA to the lung with sufficient efficacy for a sustained therapeutic effect. We have developed a self-assembling nanocomplex formulation for siRNA delivery to the airways that consists of a liposome (DOTMA/DOPE; L), an epithelial targeting peptide (P) and siRNA (R). LPR formulations were assessed for their ability to silence expression of the transcript of the gene encoding the α-subunit of the sodium channel ENaC in cell lines and primary epithelial cells, in submerged cultures or grown in air-liquid interface conditions. LPRs, containing 50 nM or 100 nM siRNA, showed high levels of silencing, particularly in primary airway epithelial cells. When nebulised these nanocomplexes still retained their biophysical properties and transfection efficiencies. The silencing ability was determined at protein level by confocal microscopy and western blotting. In vivo data demonstrated that these nanoparticles had the ability to silence expression of the α-ENaC subunit gene. In conclusion, these findings show that LPRs can modulate the activity of ENaC and this approach might be promising as co-adjuvant therapy for cystic fibrosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

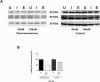
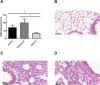
References
-
- Buchwald M, Tsui LC, Riordan JR. The search for the cystic fibrosis gene. American Journal of Physiology. 1989;257:L47–52. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

