CD49d associates with nodal presentation and subsequent development of lymphadenopathy in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia
- PMID: 28386906
- PMCID: PMC5549625
- DOI: 10.1111/bjh.14647
CD49d associates with nodal presentation and subsequent development of lymphadenopathy in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia
Abstract
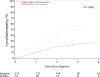
CD49d is a surface integrin that is expressed on chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL) cells, and strongly correlates with more aggressive disease. Given its association with cell-cell adhesion and leucocyte trafficking, we hypothesized that patients with high CD49d expression would experience a clinical course dominated by lymphadenopathy. CD49d expression was measured by flow cytometry and considered positive if expressed by ≥30% of CLL cells. The study included 797 newly diagnosed CLL/small lymphocytic leukaemia patients; 279 (35%) were CD49d positive. CD49d-positive patients were more likely to present with lymphadenopathy (P < 0·001); a finding that persisted after adjusting for fluorescence in situ hybridisation (FISH) and IGHV mutation status [odds ratio (OR) 2·51; 95% confidence interval (CI) 1·64-3·83; P < 0·001]. Among CLL Rai 0 patients, CD49d positivity was associated with shorter time to development of lymphadenopathy (3·2 years vs not reached, P < 0·01). This association was maintained after adjusting for either FISH [hazard ratio (HR) 2·18; 95% CI 1·25-3·81; P = 0·006) or IGHV status (HR 2·02; 95% CI 1·11-3·69; P = 0·02) individually, but was attenuated when adjusting by both (HR 1·72; 95% CI 0·88-3·38; P = 0·11).These data demonstrate that CD49d-positive CLL patients experience a disease course dominated by lymphadenopathy. These findings could have implications for therapy selection and disease monitoring.
Keywords: CD49d; chronic lymphocytic leukaemia; lymphadenopathy; small lymphocytic lymphoma.
© 2017 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Aydin S, Grabellus F, Eisele L, Mollmann M, Hanoun M, Ebeling P, Moritz T, Carpinteiro A, Nuckel H, Sak A, Gothert JR, Duhrsen U, Durig J. Investigating the role of CD38 and functionally related molecular risk factors in the CLL NOD/SCID xenograft model. European Journal of Haematology. 2011;87:10–19. - PubMed
-
- Bairey O, Zimra Y, Rabizadeh E, Shaklai M. Expression of adhesion molecules on leukemic B cells from chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients with predominantly splenic manifestations. The Israel Medical Association Journal: IMAJ. 2004;6:147–151. - PubMed
-
- Bomben R, Dal Bo M, Capello D, Benedetti D, Marconi D, Zucchetto A, Forconi F, Maffei R, Ghia EM, Laurenti L, Bulian P, Del Principe MI, Palermo G, Thorselius M, Degan M, Campanini R, Guarini A, Del Poeta G, Rosenquist R, Efremov DG, Marasca R, Foa R, Gaidano G, Gattei V. Comprehensive characterization of IGHV3-21-expressing B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia: an Italian multicenter study. Blood. 2007;109:2989–2998. - PubMed
-
- Buchner M, Baer C, Prinz G, Dierks C, Burger M, Zenz T, Stilgenbauer S, Jumaa H, Veelken H, Zirlik K. Spleen tyrosine kinase inhibition prevents chemokine- and integrin-mediated stromal protective effects in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 2010;115:4497–4506. - PubMed
-
- Buggins AG, Pepper C, Patten PE, Hewamana S, Gohil S, Moorhead J, Folarin N, Yallop D, Thomas NS, Mufti GJ, Fegan C, Devereux S. Interaction with vascular endothelium enhances survival in primary chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells via NF-kappaB activation and de novo gene transcription. Cancer Research. 2010;70:7523–7533. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

