Novel protein kinase targets in vascular smooth muscle therapeutics
- PMID: 28388507
- PMCID: PMC5478428
- DOI: 10.1016/j.coph.2017.03.003
Novel protein kinase targets in vascular smooth muscle therapeutics
Abstract
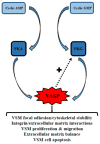
Many signaling factors have been identified over the years that serve as mechanistic foundations for the pathogenesis and/or maintenance of cardiovascular disease (CVD). Of these, cyclic nucleotide-driven protein kinases in vascular smooth muscle (VSM) are of essential importance. Comprised primarily of cyclic AMP-dependent and cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinases, these ubiquitous signaling molecules have capacity to operate through numerous downstream effectors including vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein (VASP) to control aberrant VSM growth elemental to CVD. As more information is gathered regarding genetic, biochemical, molecular and cellular makeup of CVD including VSM cyclic nucleotide-dependent protein kinases and VASP, advances will be made in precision medicine by identifying more precise therapeutic targets to enhance clinical decision making.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Roskoski R., Jr A historical overview of protein kinases and their targeted small molecule inhibitors. Pharmacol Res. 2015;100:1–23. This excellent updated biochemical and pharmacological review summarizes the current state of knowledge for the therapeutic potential of small molecule inhibitors for a variey of members in the expansive protein kinase family. This comprehensive article includes discussion of the structure and function of diverse protein kinases, their signal transduction cascades, and details of clinical drug discovery for small molecule protein kinase inhibitors. - PubMed
-
- Adderley SP, Joshi CN, Martin DN, Mooney S, Tulis DA. Multiple kinase involvement in the regulation of vascular growth. In: Da Silva Xavier G, editor. Advances in Protein Kinases. InTech Open Access Publishers; 2012. pp. 131–150. This basic science article presents an overview of the roles of cyclic nucleotide-dependent protein kinases in vascular growth with inclusion of original data supporting growth-mitigating properties of differentially phosphorylated VASP in VSM.
-
- Manning G, Whyte DB, Martinez R, Hunter T, Sudarsanam S. The protein kinase complement of the human genome. Science. 2002;298:1912–1934. - PubMed
-
- Ubersax JA, Ferrell JE. Mechanisms of specificity in protein phosphorylation. Nature Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8:530–541. - PubMed
-
- Cohen P. Protein kinase inhibitors for the treatment of disease: the promise and the problems. In: Pinna LA, Cohen PTW, editors. Inhibitors of protein kinases and protein phosphatases. Vol. 167. Springer-Verlag; Berlin Heidelberg: 2005. pp. 1–7.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

