Effect of teriparatide (rh-PTH 1-34) versus bisphosphonate on the healing of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture: A retrospective comparative study
- PMID: 28388910
- PMCID: PMC5384154
- DOI: 10.1186/s12891-017-1509-1
Effect of teriparatide (rh-PTH 1-34) versus bisphosphonate on the healing of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture: A retrospective comparative study
Abstract
Background: Teriparatide (recombinant human parathyroid hormone 1-34) is increasingly used for the treatment of severe osteoporosis because it stimulates bone formation and may potentially enhance fracture healing. The objective of this study was to investigate the effects of teriparatide versus a bisphosphonate on radiographic outcomes in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures (OVCF).
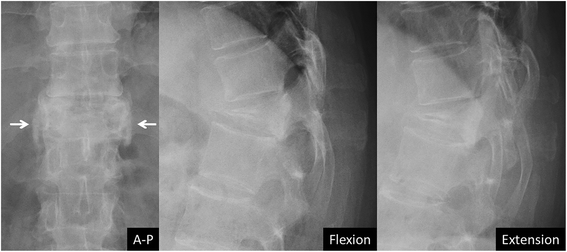
Methods: A total of 98 patients undergoing non-operative treatment for recent single-level OVCF were reviewed retrospectively. Thirty-eight patients were treated by a once-daily subcutaneous injection of 20 micrograms of teriparatide (TPD group), whereas 60 patients received 35 mg of alendronate weekly (BP group). Except for these medications, the same treatment protocol was applied to both groups. The radiographic assessments included union status, vertebral kyphosis, and mid-vertebral body height. The rates of fracture site surgical intervention were also compared between the two groups. The mean follow-up period was 27 months (median 22.5, range 2 - 75 months).
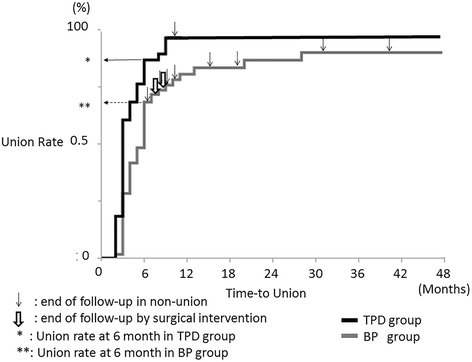
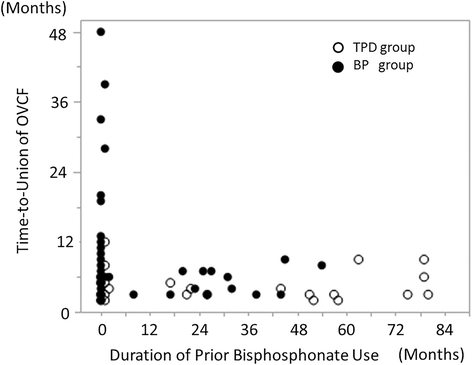
Results: Cox regression analysis showed that TPD reduced the time-to-union (adjusted relative hazard ratio: 1.86, 95% C.I.: 1.21 - 2.83). The union rate at six months after treatment was 89% in the TPD group and 68% in the BP group; the surgical intervention rate was significantly higher in the TPD group (p = 0.026, adjusted odds ratio: 8.15, 95% C.I.: 2.02 - 43.33). The change in local kyphosis was 4.6° in the TPD group and 3.8° in the BP group (p = 0.495, paired t-test). The change of mid-vertebral body height was 4.4 mm in the TPD group and 3.4 mm in the BP group (p = 0.228, paired t-test). Fracture site surgical interventions were not required in the TPD group; however, two patients in the BP group eventually underwent surgical treatment for symptomatic non-union or vertebral collapse.
Conclusions: This retrospective study suggests that teriparatide may enhance fracture healing and improve the union rate in OVCF.
Keywords: Bisphosphonates; Osteoporosis; Osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture; Recombinant human parathyroid hormone 1–34; Teriparatide; Union rate.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Aggravation of spinal cord compromise following new osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture prevented by teriparatide in patients with surgical contraindications.Osteoporos Int. 2016 Nov;27(11):3309-3317. doi: 10.1007/s00198-016-3651-2. Epub 2016 May 31. Osteoporos Int. 2016. PMID: 27245056 Clinical Trial.
-
Teriparatide alone versus vertebroplasty on pain control and radiographic outcomes after osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture.Eur Spine J. 2024 Aug;33(8):3284-3290. doi: 10.1007/s00586-024-08349-9. Epub 2024 Jun 27. Eur Spine J. 2024. PMID: 38937348
-
Comparison of once-weekly teriparatide and alendronate against new osteoporotic vertebral fractures at week 12.J Bone Miner Metab. 2020 Jan;38(1):44-53. doi: 10.1007/s00774-019-01023-x. Epub 2019 Jul 11. J Bone Miner Metab. 2020. PMID: 31297652 Clinical Trial.
-
Use of teriparatide in osteoporotic fracture patients.Injury. 2016 Jan;47 Suppl 1:S36-8. doi: 10.1016/S0020-1383(16)30009-2. Injury. 2016. PMID: 26768289 Review.
-
Effect of medications on prevention of secondary osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture, non-vertebral fracture, and discontinuation due to adverse events: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019 Aug 31;20(1):399. doi: 10.1186/s12891-019-2769-8. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019. PMID: 31472671 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Delayed-onset radiculopathy caused by a retropulsed bone fragment after percutaneous kyphoplasty: report of four cases and literature review.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022 Jun 2;23(1):529. doi: 10.1186/s12891-022-05472-w. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022. PMID: 35655255 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy of Three Teriparatide Preparations and Romosozumab, Osteogenesis Promoters, in the Treatment of Fresh Vertebral Fractures: A Retrospective Observational Study.Drugs Real World Outcomes. 2023 Dec;10(4):631-637. doi: 10.1007/s40801-023-00385-z. Epub 2023 Sep 28. Drugs Real World Outcomes. 2023. PMID: 37768478 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of osteoanabolic agents (teriparatide and romosozumab) with bisphosphonates in prevention of subsequent vertebral fractures in patients treated for osteoporotic vertebral fracture for 12 months: An observational cohort study.Bone Rep. 2024 Apr 12;21:101762. doi: 10.1016/j.bonr.2024.101762. eCollection 2024 Jun. Bone Rep. 2024. PMID: 38650912 Free PMC article.
-
The Healing and therapeutic effects of perioperative bisphosphonate use in patients with fragility fractures: meta-analysis of 19 clinical trials.Osteoporos Int. 2024 Nov;35(11):1897-1907. doi: 10.1007/s00198-024-07191-5. Epub 2024 Aug 8. Osteoporos Int. 2024. PMID: 39115687 Free PMC article.
-
Osteoporosis Drug Treatment Update.Rev Bras Ortop (Sao Paulo). 2021 Oct 28;56(5):550-557. doi: 10.1055/s-0040-1714219. eCollection 2021 Oct. Rev Bras Ortop (Sao Paulo). 2021. PMID: 34733425 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dempster DW, Cosman F, Parisien M, Shen V, Lindsay R. Anabolic actions of parathyroid-hormone on bone. Endocr Rev. 1993;14(6):690–709. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

