Microfluidic Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy of Carbon Composite Nanofluids
- PMID: 28389655
- PMCID: PMC5429664
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-00760-1
Microfluidic Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy of Carbon Composite Nanofluids
Abstract
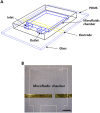
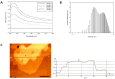
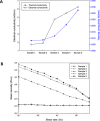
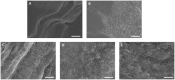
Understanding the internal structure of composite nanofluids is critical for controlling their properties and engineering advanced composite nanofluid systems for various applications. This goal can be made possible by precise analysis with the help of a systematic robust platform. Here, we demonstrate a microfluidic device that can control the orientation of carbon nanomaterials in a suspension by applying external fields and subsequently examine the electrochemical properties of the fluids at microscale. Composite nanofluids were prepared using carbon nanomaterials, and their rheological, thermal, electrical, and morphological characteristics were examined. The analysis revealed that microfluidic electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) in the device offered more reliable in-depth information regarding the change in the microstructure of carbon composite nanofluids than typical bulk measurements. Equivalent circuit modelling was performed based on the EIS results. Furthermore, the hydrodynamics and electrostatics of the microfluidic platform were numerically investigated. We anticipate that this microfluidic approach can serve as a new strategy for designing and analyzing composite nanofluids more efficiently.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Acid-functionalized carbon nanofibers for high stability, thermoelectrical and electrochemical properties of nanofluids.J Colloid Interface Sci. 2018 Jun 15;520:50-57. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2018.02.042. Epub 2018 Mar 3. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2018. PMID: 29529460
-
Surface Modification Approach to TiO2 Nanofluids with High Particle Concentration, Low Viscosity, and Electrochemical Activity.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015 Sep 23;7(37):20538-47. doi: 10.1021/acsami.5b05864. Epub 2015 Sep 10. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015. PMID: 26322861
-
Nanofluids research: key issues.Nanoscale Res Lett. 2010 May 22;5(8):1241-52. doi: 10.1007/s11671-010-9638-6. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2010. PMID: 20676214 Free PMC article.
-
Carbon-Based Nanofluids and Their Advances towards Heat Transfer Applications-A Review.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021 Jun 21;11(6):1628. doi: 10.3390/nano11061628. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34205801 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Review on thermal properties of nanofluids: Recent developments.Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2015 Nov;225:146-76. doi: 10.1016/j.cis.2015.08.014. Epub 2015 Sep 3. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2015. PMID: 26391519 Review.
Cited by
-
Modeling and optimization of thermal conductivity and viscosity of MnFe2O4 nanofluid under magnetic field using an ANN.Sci Rep. 2017 Dec 12;7(1):17369. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-17444-5. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29234090 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient photocatalytic activity of ZnO/GO/CuO nanocomposite with solar light for reduction of hexavalent chromium.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;15(1):20780. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-05790-8. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40594225 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

