Neonatal alcohol exposure reduces number of parvalbumin-positive interneurons in the medial prefrontal cortex and impairs passive avoidance acquisition in mice deficits not rescued from exercise
- PMID: 28391014
- PMCID: PMC5485852
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2017.03.058
Neonatal alcohol exposure reduces number of parvalbumin-positive interneurons in the medial prefrontal cortex and impairs passive avoidance acquisition in mice deficits not rescued from exercise
Abstract
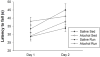
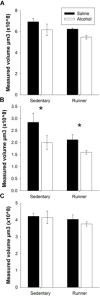
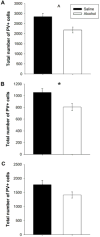
Developmental alcohol exposure causes a host of cognitive and neuroanatomical abnormalities, one of which is impaired executive functioning resulting from medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) damage. This study determined whether third-trimester equivalent alcohol exposure reduced the number of mPFC GABAergic parvalbumin-positive (PV+) interneurons, hypothesized to play an important role in local inhibition of the mPFC. The impact on passive avoidance learning and the therapeutic role of aerobic exercise in adulthood was also explored. Male C57BL/6J mice received either saline or 5g/kg ethanol (two doses, two hours apart) on PD 5, 7, and 9. On PD 35, animals received a running wheel or remained sedentary for 48days before behavioral testing and perfusion on PD 83. The number of PV+ interneurons was stereologically measured in three separate mPFC subregions: infralimbic, prelimbic and anterior cingulate cortices (ACC). Neonatal alcohol exposure decreased number of PV+ interneurons and volume of the ACC, but the other regions of the mPFC were spared. Alcohol impaired acquisition, but not retrieval of passive avoidance, and had no effect on motor performance on the rotarod. Exercise had no impact on PV+ cell number, mPFC volume, or acquisition of passive avoidance, but enhanced retrieval in both control and alcohol-exposed groups, and enhanced rotarod performance in the control mice. Results support the hypothesis that part of the behavioral deficits associated with developmental alcohol exposure are due to reduced PV+ interneurons in the ACC, but unfortunately exercise does not appear to be able to reverse any of these deficits.
Keywords: anterior cingulate cortex; executive function; fear; fetal alcohol spectrum disorders; inhibition; running.
Copyright © 2017 IBRO. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

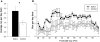
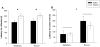
Similar articles
-
Voluntary exercise partially reverses neonatal alcohol-induced deficits in mPFC layer II/III dendritic morphology of male adolescent rats.Synapse. 2015 Aug;69(8):405-15. doi: 10.1002/syn.21827. Epub 2015 Jun 17. Synapse. 2015. PMID: 25967699 Free PMC article.
-
Behavioral deficits induced by third-trimester equivalent alcohol exposure in male C57BL/6J mice are not associated with reduced adult hippocampal neurogenesis but are still rescued with voluntary exercise.Behav Brain Res. 2016 Nov 1;314:96-105. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2016.07.052. Epub 2016 Aug 1. Behav Brain Res. 2016. PMID: 27491590 Free PMC article.
-
Parvalbumin-Positive Interneurons in the Medial Prefrontal Cortex Regulate Stress-Induced Fear Extinction Impairments in Male and Female Rats.J Neurosci. 2023 May 31;43(22):4162-4173. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1442-22.2023. Epub 2023 May 1. J Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37127359 Free PMC article.
-
Age- and sex-specific effects of stress on parvalbumin interneurons in preclinical models: Relevance to sex differences in clinical neuropsychiatric and neurodevelopmental disorders.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2021 Dec;131:1228-1242. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2021.10.031. Epub 2021 Oct 27. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2021. PMID: 34718048 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sex differences in the rodent medial prefrontal cortex - What Do and Don't we know?Neuropharmacology. 2024 May 1;248:109867. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2024.109867. Epub 2024 Feb 20. Neuropharmacology. 2024. PMID: 38387553 Review.
Cited by
-
Voluntary alcohol consumption during distinct phases of adolescence differentially alters adult fear acquisition, extinction and renewal in male and female rats.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Oct 5:2023.10.03.560757. doi: 10.1101/2023.10.03.560757. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Stress. 2023 Nov;26(1):2278315. doi: 10.1080/10253890.2023.2278315. PMID: 37873067 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Deliberative Behaviors and Prefrontal-Hippocampal Coupling are Disrupted in a Rat Model of Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jul 29:2024.07.28.605480. doi: 10.1101/2024.07.28.605480. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: J Neurosci. 2025 Mar 05;45(10):e1241242025. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1241-24.2025. PMID: 39131304 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Impact of prenatal alcohol exposure on intracortical myelination and deep white matter in children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder.Neuroimage Rep. 2022 Mar;2(1):100082. doi: 10.1016/j.ynirp.2022.100082. Epub 2022 Jan 18. Neuroimage Rep. 2022. PMID: 37284413 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term effects of low prenatal alcohol exposure on GABAergic interneurons of the murine posterior parietal cortex.Alcohol Clin Exp Res (Hoboken). 2023 Dec;47(12):2248-2261. doi: 10.1111/acer.15210. Epub 2023 Oct 27. Alcohol Clin Exp Res (Hoboken). 2023. PMID: 38151788 Free PMC article.
-
Heterozygous Deletion of Epilepsy Gene KCNQ2 Has Negligible Effects on Learning and Memory.Front Behav Neurosci. 2022 Jul 19;16:930216. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2022.930216. eCollection 2022. Front Behav Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35928789 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aksu I, Baykara B, Ozbal S, Cetin F, Sisman AR, Dayi A, Gencoglu C, Tas A, Buyuk E, Gonenc-Arda S, Uysal N. Maternal treadmill exercise during pregnancy decreases anxiety and increases prefrontal cortex VEGF and BDNF levels of rat pups in early and late periods of life. Neuroscience letters. 2012;516:221–225. - PubMed
-
- Albrechet-Souza L, Borelli KG, Carvalho MC, Brandao ML. The anterior cingulate cortex is a target structure for the anxiolytic-like effects of benzodiazepines assessed by repeated exposure to the elevated plus maze and Fos immunoreactivity. Neuroscience. 2009;164:387–397. - PubMed
-
- Almada RC, Coimbra NC, Brandao ML. Medial Prefrontal Cortex Serotonergic and Gabaergic Mechanisms Modulate the Expression of Contextual Fear: Intratelencephalic Pathways and Differential Involvement of Cortical Subregions. Neuroscience. 2015;284:988–997. - PubMed
-
- Arndt SS, Laarakker MC, van Lith HA, van der Staay FJ, Gieling E, Salomons AR, van’t Klooster J, Ohl F. Individual housing of mice–impact on behaviour and stress responses. Physiology & behavior. 2009;97:385–393. - PubMed
-
- Berry A, Bellisario V, Capoccia S, Tirassa P, Calza A, Alleva E, Cirulli F. Social deprivation stress is a triggering factor for the emergence of anxiety- and depression-like behaviours and leads to reduced brain BDNF levels in C57BL/6J mice. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2012;37:762–772. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

